BUDGET 2023-24 has cheered up Indian Industry Leaders and have hailed it as “prudent”, “positive” and “progressive”. The Budget has a clear vision with 7 Priorities or Saptrishi as India enters in the “Amrit Kaal”. The modifications under the new tax regime has provided relief to common man which will certainly boost consumption. The overall perspective of the BUDGET 2023-24 is positive and includes great optimism at every stages for economic growth. This is the year where Finance Minister Mrs. Nirmala Sitharaman has used many of the Sanskrit terms like “Shree Anna”, “Panchamrit” and many more which makes this budget unique on its own.
SO HERE IS THE BUDGET 2023-24 ANALYSIS
PART A
The word Amrit Kaal was coined by Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi in the year 2021 during the festivities of 75th Independence Day. While announcing a new blue print for India’s next 25 years, PM Modi used this phrase. Amrit Kaal has a goal of improving quality of life for Indian habitants and close development gap between rural and urban areas.
The term “Amrit Kaal” comes from Vedic astrology. It refers to a crucial period when humans enjoy greater pleasure. It means the most fortunate time to begin any work.
BUDGET 2023-24 was presented by Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, the Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs. While presenting the budget she emphasized that Indian economy is on the right track and despite challenges it is heading towards a bright future.
Finance Minister said that this Budget hopes to build on the foundation laid in the previous budget and the blueprint drawn for India@100. This Budget envisions a prosperous and inclusive India, in which the fruits of development will be enjoyed by all the citizens, especially youth, women, farmers, OBCs, Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribes.
While presenting the Budget, Mrs. Nirmala Sitharaman also said that during the nine years of the government, Indian economy has increased in size from being 10th to 5th largest in the world. India has significantly improved its position as a well governed and innovative country with a conducive environment for business.
India has now a rising profile due to several accomplishments like World Class Digital Public Infrastructure namely Aadhaar, Co-win and UPI; Covid-19 vaccination drive, proactive roles in frontier areas such as achieving the climate related goal, mission LiFE, and National Hydrogen Mission.
She Also Pointed Out Certain Points Mentioned Below Before Beginning The Budget
- During Covid-19 pandemic, Government ensured that no one goes to the bed hungry. Free supply of food grains to over 80 Crore persons for 28 months. Government is implementing from 1st January 2023, a scheme to supply free food grains to all Antyodha and priority households for the next one year, under PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY). This entire expenditure of Rs 2 Lakh crore will be borne by the government.
- During the time of challenges, the G20 Presidency gives India a unique opportunity to strengthen its role in the world economy. With the theme of ‘Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’.
- Government has put in efforts since 2014 and have ensured that all citizens of the country gets a better quality of life of dignity. Per Capita Income has more than doubled to Rs 1.97 lakh. The economy has become a lot more formalized as reflected in the EPFO membership.
- The Finance Minister also pointed out that efficient implementation of many schemes with universalization of target benefits has resulted in the inclusive development. Some schemes such as 7 crore household toilets under Swachh Bharat Mission, 9.6 crore LPG connections under Ujjawala, 220 crore Covid vaccinations of 102 crore persons, 47.8 crore PM Jan Dhan Bank Accounts, Insurance cover for 44.6 crore persons under PM Suraksha Bima and PM Jeevan Jyoti Yojana, and Cash transfer of Rs 2.2 lakh crore to over 11.4 crore farmers under PM Kisan Samman Nidhi has helped to achieve this.
BUDGET 2023-24- AN OVERVIEW
The Amrit Kaal Budget has three vision for Empowered and Inclusive Economy
The Amrit Kaal Budget includes technology driven and knowledge based economy with strong public finances and a robust financial sector and to achieve this, Jan Bhagidhari through Sabka Sath Sabka Prayas is essential. This can be achieved through the three visions mentioned above that is Opportunities for citizens with focus on youth, Growth in Job creation, Strong and Stable Macro Economic Environment
The Finance Minister also discussed about the four opportunities that be utilized during Amrit Kaal which are as follows
- Economic Empowerment of Women: Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihood Mission has become successful by mobilizing rural women into 81 lakh Self Help Groups and also these groups will reach the next stage of economic empowerment through formation of large producer enterprises or collectives with each having several thousand members and managed professionally.
- PM VIshwakarma KAushal Samman (PM VIKAS):For centuries, traditional artisans and craftspeople, who work with their hands using tools, have brought renown for India and they are generally referred to as VIshwakarma. The art and handicraft created by them represents the true spirit of Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
- Tourism:The Finance Minister said that the country promotes for domestic as well as foreign tourists, as there is a large potential in tourism. She also added that the sector holds huge opportunities for jobs and entrepreneurship for youth in particular and emphasized that promotion of tourism will be taken up on mission mode, with active participation of states, convergence of government programmes and public-private partnerships.
- Green Growth: Dwelling on the subject of Green Growth, the FM said that India is implementing many programmes for green fuel, green energy, green farming, green mobility, green buildings, and green equipment, and policies for efficient use of energy across various economic sectors. These green growth efforts help in reducing carbon intensity of the economy and provides for largescale green job opportunities, she added.
BUDGET 2023-24 has 7 major priorities known as Saptrishi which are listed below
So the Saptrishi can be described in following way
“IF YOU GRIP”
I – INCLUSIVE DEVELOPMENT
F- FINANCIAL SECTOR
YOU- YOUTH POWER
G -GREEN GROWTH
R -REACHING THE LAST MILE
I -INFRASTRUCTURE AND INVESTMENT
P – UNLEASHING THE POTENTIAL
PRIORITY 1- INCLUSIVE DEVELOPMENT
Inclusive Development projects include benefits such as
- 9 crore drinking water connections to rural houses
- Cash transfer of Rs 2.2 lakh crore to over 11.4 crore Farmers under PM-KISAN.
- Insurance cover for 44.6 crore persons under PMSBY and PMJJY.
- 8 crore PM Jan Dhan bank accounts.
- 220 crore Covid Vaccinations of 102 crore persons.
- 6 Crore LPG connections under Ujjawala.
- 7 Crore household toilets constructed under SBM.
Farmers, Women, Youth, Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes such as OBC, Divyangjan (PWD) and economically weaker Sections (EWS) are specifically covered in Inclusive Development. Overall priority for the underprivileged and sustained focus on Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh and the North East Region is also included. It has two prolonged strategy which was first unveiled in 2019 like Incentivizing the private sector thus creating jobs and pushing growth and “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance” increasing capex and raising more revenues via disinvestment ,
There are three categories which is included in Inclusive Development –Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas
- Agriculture
- Digital Public Infrastructure for agriculture will be built as an open source, open standard and interoperable public good resulting in good farmer centric solutions, relevant information for crop planning and health, Better access to farm inputs, credit and insurance and growth support of the agri-tech industry and start-ups.
- Funding for Agri-Startups: Agriculture Accelerator Fund will be set up to encourage agri startups by young entrepreneurs in rural areas.
- Agri Credit target to be increased to 20 lakh crore with focus on animal husbandry dairy and fisheries. A new sub scheme of PM Matsya Sampada Yojana with targeted investment of Rs 6000 crore will be launched for fishermen , fish vendors and MSME’s.
- Horticulture: Aatmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme will be launched to boost availability of disease free, quality planting material for high value horticulture crops at an outlay of Rs 2200 crore.
- Millets– To make India a global hub for “Shree Anna”, the Indian Institute of Millet Research, Hyderabad will be supported as Centre of Excellence for sharing best practices research and technologies at the international level.
- Agri Co-operatives- To fulfill the vision of “ Sahakar Se Samriddhi”, the Government plans to establish decentralized storage capacity and set up multiple co-operative societies in uncovered villages over the 5 years.
- Education and Skilling
- Revamped Teachers training via District Institutes of Education and Training
- National Digital library to be set up for children and adolescents
- States will be encouraged to set up physical Libraries at Panchayat and ward levels.
- Health
- 157 new nursing colleges will be established in co-location with the existing 157 medical colleges established since 2014.
- Sickle Cell Anaemia elimination mission to be launched. New Programme to promote research in Pharmaceuticals to be launched.
- Joint Public and Private Medical Research to be encouraged via select ICMR Labs.
PRIORITY 2- FINANCIAL SECTOR
Credit Guarantee Scheme: In 2022, the credit guarantee scheme for MSMEs was revamped and will take effect from 1st April 2023 through infusion of Rs 9000 crore in the corpus. This will enable additional collateral free guaranteed credit of Rs 2 lakh crore. The cost of credit will be reduced by about 1%.
Financial Information Registry: A National Financial Information Registry will be set up to serve as the central repository of financial and Ancillary Information. This will facilitate efficient flow of credit to promote financial inclusion and foster financial stability. A new legislative framework designed in consultation with the RBI will govern this credit public infrastructure.
Small Saving Scheme: In the honor of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav, a new one time small saving scheme, Mahila Samman Saving Certificate will be made available for a period of two years up to March 2025. This will offer deposit facility up to Rs 2 Lakh in the name of women or girls with partial withdrawal option. The maximum deposit limit for Senior Citizen Saving Scheme will be enhanced from Rs 15 lakh to Rs 30 Lakh. The maximum deposit limit for the Monthly Income Account Scheme will be enhanced from Rs 4.5 lakh to Rs 9Lakh (for single account) and from Rs 9 lakh to Rs 15 lakh (for joint account)
PRIORITY 3- YOUTH POWER
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
On the Job training, industry partnership, new age courses like AI, robotics, mechatronics, 3D printing, drones etc.
- Skill India Digital Platform
Expanding digital ecosystem to enable demand based formal skilling, linking with employers and facilitating access to entrepreneurship schemes.
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme
To provide stipend support to 47 lakh youth in three years.
- Boosting Tourism
50 destinations to be selected and developed as complete package for domestic and foreign tourists.
- Setting Up of Unity Malls in the State Capital
For promotion and sale of ODOPs (One District, One Product), GI and handicraft products.
PRIORITY 4 – GREEN GROWTH
- National Green Hydrogen Mission
An outlay of Rs 19700 crores has been allocated to the National Green Hydrogen Mission to facilitate transition of the economy to low carbon intensity and reduce dependence on fossil fuel imports and make the country assume technology and market leadership in this sunrise sector. The target is to reach an annual production of 5 MMT by 2030.
- GOBARdhan Scheme :
500 new waste to wealth plants under GOBARdhan Scheme will be established to promote Circular Economy which includes 200 compressed biogas CBG plants and 300 community cluster based plants. Total investment here would be Rs 10,000 crore. In due course a 5% CBG mandate will be introduced for all organizations marketing natural and biogas.
- Bhartiya Prakritik Kheti Bio-Input Resource Centers:
Over the next 3 years, the Centre will facilitate 1 crore farmers to adopt natural farming by setting up 10,000 Bio-Input Resource Centres, creating a national-level distributed micro-fertilizer and pesticide manufacturing network.
- Other Investments in Green Energy:
Rs. 35,000 crore for priority capital investments towards energy transition and net zero objectives, and energy security (Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas). Battery Energy Storage Systems with capacity of 4,000 MWH to be supported with Viability Gap Funding. Rs 20,700 crore (central support – Rs 8,300 crore) for inter-state transmission system for evacuation and grid integration of 13 GW renewable energy from Ladakh.
PRIORITY 5- REACHING THE LAST MILE
- New ‘Aspirational Blocks Programme’:
Building on the success of the Aspirational Districts Programme, the Aspirational Blocks Programme was recently launched covering 500 blocks. It is aimed at improving the performance of areas across multiple domains such as health, nutrition, education, agriculture, water resources, financial inclusion, skill development, and basic infrastructure.
- PM PVTG Development Mission:
To improve socio-economic conditions of the Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission will be launched. An amount of Rs 15,000 crore will be made available to implement the Mission in the next 3 years under the Development Action Plan for the Scheduled Tribes. The Centre will also recruit 38,800 teachers and support staff for the 740 Eklavya Model Residential Schools, serving 3.5 lakh tribal students.
- Water for Drought Prone Region:
In the drought prone central region of Karnataka, central assistance of Rs 5,300 crore will be given to the Upper Bhadra Project to provide sustainable micro irrigation and filling up of surface tanks for drinking water.
- Other Initiatives:
The outlay for PM Awas Yojana is being enhanced by 66% to over Rs 79,000 crore. A ‘Bharat Shared Repository of Inscriptions (Bharat SHRI)’ will be set up in a digital epigraphy museum, with digitization of 1 lakh ancient inscriptions in the first stage.
PRIORITY 6- INFRASTRUCTURE AND INVESTMENT
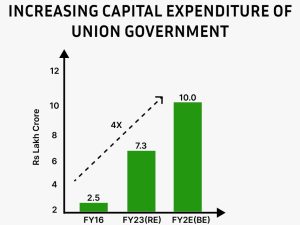
- Increase in Capex for Infra:
Capital investment outlay increased for the third consecutive year – by 33% to Rs 10 lakh crore making it 3.3% of GDP. The ‘Effective Capital Expenditure’ is budgeted at Rs 13.7 lakh crore – 4.5% of GDP.
- Support to State Govts for Cap-Investment:
The Government has decided to continue the 50-year interest free loan to state governments for one more year to spur investment in infrastructure and to incentivize them for complementary policy actions. The enhanced outlay for this is Rs 1.3 lakh crore.
- Railways:
A capital outlay of Rs 2.40 lakh crore has been provided for the Railways – the highest ever outlay and about 9 times the outlay made in 2013- 14.
- Aviation:
50 additional airports, heliports, water aerodromes and advanced landing grounds will be revived for improving regional air connectivity.
- Other Transportation Projects:
100 critical transport infrastructure projects, for last and first mile connectivity for ports, coal, steel, fertiliser, and food grains sectors have been identified and will be taken up on priority with investment of Rs 75,000 crore, including Rs 15,000 crore from private sources. An Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF) will be established through use of priority sector lending shortfall. UIDF will be managed by the National Housing Bank, and will be used by public agencies to create urban infrastructure in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities. Rs 10,000 crore on a yearly basis will be allocated for this purpose.
PRIORITY 7- UNLEASHING THE POTENTIAL
- Reduced Compliances and Jan Vishwas Bill:
To enhance ease of doing business, more than 39,000 compliances have been reduced and more than 3,400 legal provisions have been decriminalized under the amendments to the Companies Act 2013. To further the trust-based governance, the Government introduced the Jan Vishwas Bill to amend 42 Central Acts.
- Centres of Excellence for AI:
To realize the vision of “Make AI in India and Make AI work for India”, three Centres of excellence for Artificial Intelligence will be set-up in top educational institutions.
- National Data Governance Policy:
To facilitate innovation and research by start-ups and academia, a National Data Governance Policy will be brought out, which will enable access to anonymized data.
- Digilocker for Data Sharing:
An Entity Digi Locker will be set up for use by MSMEs, large business and charitable trusts for storing and sharing documents online securely, whenever needed, with various authorities, regulators, banks and other business entities.
- Resolving Disputes:
Vivad se Vishwas: Less stringent contract execution for MSME. Easier and standardized settlement scheme enabling faster settlement of contractual disputes of Govt and Govt undertakings.
e-Courts: Phase III of e-courts will be launched for effective administration of justice.
- 5G Technology:
100 labs for developing applications using 5G services will be set up in engineering institutions to realize a new range of opportunities, business models, and employment potential. The labs will cover, among others, applications such as smart classrooms, precision farming, intelligent transport systems, and healthcare apps.
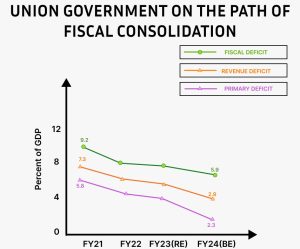
WHAT IS THE STATUS OF FISCAL MANAGEMENT?
- Utilising of Funds for Capital Expenditure
The Finance Minister stated that all states must utilize their fifty year loan for capital expenses by the end of 2023-24. Most of this will happen at the discretion of states but a part will be conditional on states designated for the purpose such as
- Replacing outdated government vehicles
- Improving urban planning
- Making urban local bodies eligible for obtaining municipal bonds
- Building housing for police officers
- Constructing Unity Malls
- Creating libraries and digital infrastructure for children and adolescents
- Contributing to the capital expenses of central schemes.
- Fiscal Deficit Allowed to States:
States are allowed to have a deficit of 3.5% of their Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP), with 0.5% of this amount specifically designated for power sector reforms.
- Revised Estimates 2022-23:
- Total receipts, (excluding borrowings): Rs 24.3 lakh crore
- Net tax receipt: Rs 20.9 lakh crore.
- Total expenditure: Rs 41.9 lakh crore
- Capital expenditure: Rs 7.3 lakh crore.
- Fiscal deficit: 6.4% of GDP.
- BUDGET ESTIMATES 2023-24:
Sr. No | Estimates | Amount |
1 | Total estimated receipts (excluding borrowings) | Rs 27.2 lakh crore |
2 | Total estimated expenditure | Rs 45 lakh crore |
3 | Net tax receipts | Rs 23.3 lakh crore. |
4 | Fiscal deficit: | 5.9% of GDP. |
To finance the fiscal deficit in 2023-24 the net market borrowings from dated securities are estimated at Rs 11.8 lakh crore. The gross market borrowings are estimated at Rs 15.4 lakh crore. Also, the government is committed to sticking to this plan to reduce the fiscal deficit to below 4.5% by 2025-26.
PART B
The finance Minister Mrs. Nirmala Sitharaman provided major relief to the tax payers. The indirect tax proposals contained in the budget aims to promote exports enhance domestic value addition, encourage green energy and mobility.
PERSONAL INCOME TAX
There are five major announcements relating to personal income tax. The revised rebate limit as per the new tax regime is increased to Rs 7 lakh. The tax structure of the new personal tax regime has been changed by reducing number of slabs to five and increasing the tax exemption limit to Rs 3 lakh. This will provide major relief to all tax payers in the new regime.
The benefit of standard deduction has been extended to the salaried class and the pensioners including family pensioner under the new tax regime. Salaried individual will get standard deduction of ₹ 50,000 and pensioner ₹ 15,000 as per the proposal. Each salaried person with an income of ₹ 15.5 lakh or more will thus gain ₹ 52,500, from the above proposals.
The highest surcharge rate in personal income tax has been reduced from 37% to 25% in the new tax regime for income above ₹2 crore. This would result in maximum tax rate of personal income tax come down to 39% which was earlier 42.74%. The limit of tax exemption on leave encashment on retirement of non-government salaried employees has been increased from ₹3 lakh to ₹25 lakh.
The new income tax regime has been made the default tax regime. However, the citizens will continue to have the option to avail the benefit of the old tax regime.
Current and Proposed Tax Slabs:
Current Income Slab | Proposed Income Slab | Tax Rate |
Up to Rs 2.5 lakh | Up to Rs 3 lakh | Nil |
Rs 2.5 lakh to Rs 5 lakh | Rs 3 lakh to Rs 6 lakh | 5% |
Rs 5 lakh to Rs 7.5 lakh | Rs 6 lakh to Rs 9 lakh | 10% |
Rs 7.5 lakh to Rs 10 lakh | Rs 9 lakh to Rs 12 lakh | 15% |
Rs 10 lakh to Rs 12 lakh | Rs 12 lakh to Rs 15 lakh | 20% |
Rs 12 lakh to Rs 15 lakh | – | 25% |
Above Rs 15 lakh | Above Rs 15 lakh | 30% |
DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS
To reduce the compliance burden, promote entrepreneurial spirit and provide tax relief to citizens.
- 45% of the returns on tax payers portal were processed within 24 hours.
- Average processing period reduced from 93 to 16 days in 8 years.
- Processed more than 6.5 crore returns this year.
INDIRECT TAX PROPOSALS
The Indirect tax proposals mentioned in the Union Budget by Mrs. Nirmala Sitharaman emphasized on simplification of tax structure with fever tax rates so as help reducing the burden and improving tax administration. The number of basic customs duty rates on goods, other than textiles and agriculture, has been reduced from 21 to 13. There are minor changes in the basic customs duties, cesses and surcharges on items including toys, bicycles, automobiles and naphtha.
The Indirect Tax Proposals include
1. Green Mobility : To exempt excise duty on GST Paid compressed bio gas.
2. Electronics : To provide relief in customs duty on import of certain parts of mobile phones. To reduce basic customs duty on parts of open cells of TV panels to 2.5%.
3. Electricals : To increase basic customs duty on electric kitchen chimney from 7.5% to 15%. To reduce basic customs duty on chimney heat coils from 20% to 15%.
4. Chemicals and Petrochemicals : To exempt basic customs duty on chemicals and petrochemicals. To reduce basic customs duty on acid grade fluorspar and crude glycerin to 2.5%.
5. Marine Products : To reduce duty on key inputs for domestic manufacture of shrimp feed.
6. Lab Grown Diamonds : To reduce basic customs duty on seeds used in their manufacturing.
7. Precious Metals : To increase customs duties on articles made from gold and platinum. To increase import duty on silver dore, bars and articles
8. Compounded Rubber : To increase basic customs duty rate on compounded rubber from 10% to 25%.
9. Cigarettes : National Calamity Contingent Duty on specified Cigarettes to be revised upwards by about 16%
Other Tax Reforms:
STANDARD DEDUCTION:
- The new tax regime has proposed to increase the standard deductionfor salaried individuals to 50,000 rupees and the deduction for family pension up to 15,000 rupees.
MSMEs:
- The limits for presumptive taxation have been increased for micro enterprises and certain professionals as long as the amount received in cash does not exceed 5% of the total gross receipts/turnover.
- The deduction for payments made to MSMEs will only be allowed when payment is actually made to support their timely receipt of payments.
COOPERATIVES:
- New manufacturingco-operatives that start manufacturing before 31.3.2024 will have a lower tax rate of 15%.
- The limit for cash deposits and loans by Primary Agricultural Co-operative Societies and Primary Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks has been increased to 2 lakh rupees per member.
- Tax Deduction at Source (TDS) on cash withdrawals for co-operative societies has been increased to 3 crore rupees.
STARTUPS:
- The date for start-upsto receive income tax benefits has been extended to 31.3.2024. The carry forward of losses for start-ups has been increased from 7 years of incorporation to 10 years.
ONLINE GAMING:
- Taxability on online gamingwill be clarified with TDS and taxability on net winnings at the time of withdrawal or at the end of the financial year.
GOLD:
- Conversion of gold into electronic gold receipt and vice versa will not be treated as capital gains.
RATIONALISATION
- Income of authorities, boards and commissions set up by statutes of the Union or State to be exempted from income tax in certain sectors.
- Extension of period of tax benefits to funds relocating to IFSC, GIFT City till 31st March, 2025.
EXCEPTION FROM INCOME TAX:
- Income of authorities, boards and commissions set up by Union or State laws for housing, town and village development, and regulation, will be exempt from income tax.
- Agni veerFund has been given Exempt-Exempt-Exempt (EEE) status. Payments received by Agni veers enrolled in Agneepath Scheme, 2022 will be exempt from taxes.
- Deduction in total income will be allowed for contributions to the Agni veer Seva Nidhi account by the Agni veer or the Central Government.
EXCEPTION FROM DUTIES:
- Compressed biogascontained in blended compressed natural gas.
- Testing agencies that import vehicles, automobile parts/components, sub-systems, and tires for testing and/or certification purposes.
- Also, the deadline for the customs duty on specified machinery for lithium-ion cell manufacturing for EV batterieshas been extended to 31.03.2024.
- Denatured ethyl alcohol used in the chemical industry.
LEGISLATIVE CHANGES IN CUSTOMS LAWS:
The Customs Act, 1962 is going to be revised to set a nine-month deadline for the Settlement Commission to make a final decision after an application has been filed. The Customs Tariff Act will be revised to make the purpose and scope of Anti-Dumping Duty (ADD), Countervailing Duty (CVD), and Safeguard Measures clearer.
Changes will also be made to the Central Goods and Service Tax Act:
- The minimum amount of tax for starting a prosecution under GST will be raised from 1 crore to 2 crore. The compounding amount for tax will be reduced from 50-150% to 25-100% of the tax amount.
- Certain offences will be decriminalized.
- The filing of returns or statements will be limited to a maximum of three years from the due date.
- Unregistered suppliers and composition taxpayers will be allowed to make intra-state supply of goods throughE-Commerce Operators (ECOs).
RUPEE COMES FROM
RUPEE GOES TO
CONCLUSION
The Union Budget 2023-24 aims to strengthen India’s economic status. The mood behind this budget presented has been optimistic. The Indian economy is being viewed as a bright star amid crisis and economic slowdown outperforming with it peers. With this Budget India hopes to become a envisioned and prosperous country.