- Introduction to Trading Psychology
- Risk Management In Trading Psychology
- Challenges in Trading Psychology
- How to Stop Overtrading
- Common Trading Mistakes
- Disciplined Trader Success Formula
- Market Dynamics Basics
- How Trading Psychology Awareness can Improve Performance
- Strategy Plus Psychology=Success
- Resilience and Stress Response Management
- Advanced Techniques for Enhancing Trading Psychology
- Study
- Slides
- Videos
4.1.What is Overtrading??

Overtrading occurs when a business undertakes more transactions or activities than it can support with its available resources, such as cash, working capital, or inventory. This situation often arises in growing businesses that expand too quickly without adequate financial planning.
Here are some key aspects of overtrading:
- Cash Flow Problems: The business might struggle to pay its bills because its cash is tied up in inventory or receivables, leading to liquidity issues.
- Increased Debt: To sustain operations, the company may need to borrow more, leading to higher interest payments and financial strain.
- Supply Chain Strain: Overtrading can strain relationships with suppliers due to late payments or increased demand beyond what the supply chain can handle.
- Operational Inefficiency: Rapid expansion can lead to inefficiencies, such as poor customer service or mistakes in orders, as the business struggles to keep up with demand.
- Risk of Insolvency: If not managed carefully, overtrading can push a business into insolvency, where it cannot meet its financial obligations.
4.2.Ways to Stop Overtrading

To prevent or stop overtrading, businesses can implement several strategies aimed at improving financial management, operational efficiency, and strategic planning. Here are some effective ways to address and prevent overtrading:
- Improve Cash Flow Management
-
- Monitor Cash Flow Closely: Regularly track cash inflows and outflows to ensure there is enough liquidity to cover expenses.
- Accelerate Receivables: Implement measures to reduce the time it takes to collect payments from customers, such as offering discounts for early payments or tightening credit terms.
- Manage Payables Efficiently: Negotiate longer payment terms with suppliers to better align cash outflows with inflows.
- Enhance Working Capital Management
-
- Optimize Inventory Levels: Avoid holding too much stock by implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems or better forecasting demand to match supply with demand.
- Reduce Debt Levels: Pay down high-interest debts to reduce financial strain and improve liquidity.
- Strengthen Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with suppliers to negotiate favourable terms and ensure reliable supply chains.
- Scale Growth Strategically
-
- Plan for Sustainable Growth: Develop a growth strategy that aligns with the company’s financial capabilities, avoiding overly aggressive expansion that exceeds resources.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Concentrate on the most profitable and manageable areas of the business rather than diversifying too quickly.
- Seek External Funding: If expansion is necessary, consider securing external funding through equity investment or long-term loans to support growth without overstretching resources.
- Implement Strong Financial Controls
-
- Set Budget Limits: Establish and adhere to strict budgets for different business activities to control spending and avoid overextending resources.
- Regular Financial Reviews: Conduct regular financial reviews and audits to detect early signs of overtrading and take corrective action.
- Use Financial Ratios: Monitor key financial ratios such as the current ratio, quick ratio, and debt-to-equity ratio to assess the financial health of the business and identify potential overtrading risks.
- Enhance Operational Efficiency
-
- Invest in Technology: Use technology to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and reduce costs, which can help balance the business’s capacity with demand.
- Train Employees: Ensure that employees are well-trained to handle increased workloads efficiently and maintain high standards of service.
- Focus on Customer Satisfaction: Maintain high levels of customer service to prevent issues that could arise from overextending operations, such as delays or errors.
- Seek Professional Advice
-
- Consult Financial Advisors: Work with financial advisors or consultants to develop strategies to prevent overtrading and improve overall business performance.
- Regularly Review Business Plans: Continuously update and review business plans to ensure they remain aligned with the company’s current financial situation and market conditions.
4.3. Overtrading While Day Trading
Overtrading in the context of day trading refers to the excessive buying and selling of securities, often driven by the desire to capture small price movements or recover from losses. This behavior can lead to a variety of negative consequences, including increased transaction costs, emotional stress, and significant financial losses.
Causes of Overtrading in Day Trading
- Emotional Decision-Making:
-
- Fear of Missing out (FOMO): Traders may overtrade out of fear of missing potential profits, leading to impulsive decisions.
- Revenge Trading: After a loss, traders may place additional trades to quickly recover, often resulting in further losses.
- Lack of a Trading Plan:
-
- No Clear Strategy: Without a well-defined trading strategy, traders may enter and exit trades randomly, leading to overtrading.
- Ignoring Risk Management: Failing to adhere to risk management rules, such as stop-loss limits, can result in more trades than planned.
- Overconfidence:
-
- Winning Streaks: After a series of successful trades, traders might feel overconfident and start making more trades than their strategy dictates.
- Belief in Skill over Luck: Some traders overestimate their abilities, believing that frequent trading will yield better results.
- Chasing the Market:
-
- Market Volatility: During periods of high volatility, traders may be tempted to make numerous trades to capitalize on price fluctuations, leading to overtrading.
- Reacting to News: Constantly reacting to news events without proper analysis can lead to an excessive number of trades.
Consequences of Overtrading
- Increased Transaction Costs:
-
- Commissions and Fees: Frequent trades result in higher transaction costs, which can erode profits or deepen losses.
- Slippage: Rapid buying and selling can lead to slippage, where trades are executed at a less favourable price than expected.
- Emotional and Mental Stress:
-
- Decision Fatigue: Constant decision-making can lead to exhaustion, resulting in poor judgment and impulsive trades.
- Increased Anxiety: The pressure to monitor and execute numerous trades can heighten stress levels and negatively impact overall well-being.
- Reduced Profitability:
-
- Lower Win Rate: Overtrading often leads to lower-quality trades, reducing the overall win rate.
- Capital Erosion: Excessive trading can lead to small, frequent losses that accumulate over time, diminishing trading capital.
- Loss of Discipline:
-
- Deviating from Strategy: Overtrading often involves abandoning a disciplined trading approach, leading to inconsistent results.
- Risk of Ruin: Persistently overtrading without proper risk management can lead to significant financial losses, potentially wiping out the trading account.
How to Prevent Overtrading in Day Trading
- Develop a Clear Trading Plan:
-
- Set Trade Limits: Define a maximum number of trades per day or week to prevent overtrading.
- Establish Entry and Exit Criteria: Stick to predefined criteria for entering and exiting trades to avoid impulsive decisions.
- Implement Strong Risk Management:
-
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Protect against significant losses by setting stop-loss orders for every trade.
- Determine Position Size: Base position sizes on a percentage of your total capital, ensuring that individual trades don’t overexpose you to risk.
- Maintain Emotional Control:
-
- Recognize Emotional Triggers: Be aware of emotions like fear, greed, or frustration that may lead to overtrading.
- Take Breaks: Step away from the screen periodically to maintain perspective and avoid trading out of boredom or frustration.
- Track and Review Trades:
-
- Keep a Trading Journal: Document each trade, including the rationale, outcome, and emotions, to identify patterns of overtrading.
- Regularly Review Performance: Assess your trading performance regularly to ensure you’re adhering to your plan and avoiding overtrading.
- Focus on Quality, Not Quantity:
-
- Prioritize High-Probability Trades: Focus on trades that meet all your criteria rather than trying to capture every market movement.
- Stay Patient: Wait for the best trading opportunities instead of forcing trades in less-than-ideal conditions.
4.4 Relying on willpower and self-discipline
Relying on willpower and self-discipline is crucial in trading, especially for day traders who must manage emotions and adhere to strategies. However, while these traits are beneficial, they also come with challenges.
Benefits of Relying on Willpower and Self-Discipline in Trading
- Consistency in Following a Trading Plan:
-
- Adherence to Strategy: Willpower helps traders stick to their pre-defined trading strategies, ensuring consistent decision-making.
- Avoidance of Impulsive Decisions: Strong self-discipline reduces the likelihood of impulsive trades based on emotions or market noise, leading to more rational and calculated trading.
- Effective Risk Management:
-
- Control over Position Sizes: Traders with self-discipline are more likely to adhere to risk management rules, such as limiting position sizes and setting stop-loss orders.
- Minimization of Losses: By sticking to risk management practices, disciplined traders can minimize losses and protect their capital.
- Emotional Resilience:
-
- Resistance to Emotional Trading: Willpower enables traders to stay calm and focused, even in volatile markets, reducing the impact of fear, greed, and other emotions on trading decisions.
- Recovery from Losses: Self-discipline helps traders manage losses without resorting to revenge trading, maintaining a long-term perspective.
Long-Term Success:
-
- Building Good Habits: Consistent application of willpower and self-discipline can lead to the development of positive trading habits, which contribute to long-term success.
- Enhanced Focus and Concentration: Disciplined traders are more likely to maintain focus and avoid distractions, leading to better decision-making and improved trading outcomes.
Problems with Relying on Willpower and Self-Discipline in Trading
- Limited Resource:
-
- Willpower Depletion: Willpower is a finite resource that can be depleted over time, especially during stressful trading sessions. As willpower wanes, traders may struggle to maintain discipline, leading to poor decisions.
- Decision Fatigue: Constant reliance on self-discipline can lead to decision fatigue, where the ability to make sound decisions diminishes after repeated trading decisions, increasing the risk of errors.
- Increased Stress and Burnout:
-
- Emotional Strain: Continuously exerting self-discipline can lead to heightened stress and emotional strain, which can negatively affect mental health and trading performance.
- Risk of Burnout: Over-reliance on willpower to maintain discipline without adequate rest or breaks can lead to burnout, reducing the trader’s overall effectiveness and motivation.
- Rigidity in Trading:
-
- Lack of Flexibility: Excessive reliance on self-discipline can make traders overly rigid, preventing them from adapting to changing market conditions or seizing unexpected opportunities.
- Inability to Adjust Strategies: A disciplined trader might stick too rigidly to a strategy even when market conditions suggest a need for adaptation, potentially missing out on profitable trades.
- Overconfidence in Control:
-
- False Sense of Security: Traders who rely heavily on willpower may develop overconfidence in their ability to control outcomes, leading to riskier behavior and potential losses.
- Ignoring External Factors: Focusing too much on self-discipline may lead to underestimating the impact of external factors, such as market volatility or unforeseen events, which can disrupt even the best-laid plans.
- Inconsistent Application:
-
- Difficulty in Maintaining Discipline: While traders may start with strong willpower and discipline, maintaining it consistently over time can be challenging, especially in the face of prolonged market adversity.
- Potential for Relapses: Traders may experience moments of weakness, where they abandon discipline temporarily, leading to costly mistakes.
Balancing Willpower with Other Strategies
Given the limitations of relying solely on willpower and self-discipline, traders should consider integrating these traits with other strategies:
-
- Automated Trading Systems: Use technology to automate parts of the trading process, reducing the reliance on willpower for routine decisions.
- Scheduled Breaks and Rest: Incorporate regular breaks and downtime into the trading schedule to prevent burnout and decision fatigue.
- Mindfulness and Stress Management: Practice mindfulness or other stress-reduction techniques to manage emotional strain and maintain discipline without overexerting willpower.
- Diversification of Strategies: Be flexible and willing to adjust or diversify trading strategies based on market conditions, reducing the pressure on self-discipline alone to achieve success.
4.5 Common triggers to overtrading and how to deal with them
Overtrading, especially in the context of day trading, can be triggered by various psychological and emotional factors. Recognizing these triggers and learning how to manage them is essential for maintaining discipline and achieving long-term success in trading. Here are some common triggers to overtrading and strategies to deal with them:
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
Traders often feel the urge to enter trades impulsively when they see rapid price movements, fearing that they might miss out on a profitable opportunity.
How to Deal with It:
- Stick to Your Trading Plan: Rely on your predefined strategy and only enter trades that meet your criteria, regardless of market hype.
- Focus on Long-Term Goals: Remind yourself that missing one opportunity isn’t the end of your trading journey. There will always be more opportunities.
- Limit Social Media Exposure: Reduce time spent on social media platforms where others might boast about their trades, which can exacerbate FOMO.
- Revenge Trading
After experiencing a loss, a trader may feel compelled to quickly recover the lost capital by taking more trades, often with higher risk.
How to Deal with It:
- Take a Break: Step away from the trading platform after a loss to cool off and regain emotional balance before considering new trades.
- Review the Loss Objectively: Analyze the trade that resulted in a loss to understand what went wrong, without letting emotions drive your next moves.
- Set Daily Loss Limits: Establish a daily loss limit, after which you stop trading for the day, to prevent emotional decision-making.
- Overconfidence after a Winning Streak
A series of successful trades can lead to overconfidence, causing a trader to take more trades, often with larger position sizes, believing they can’t lose.
How to Deal with It:
- Review Each Trade: Even after wins, critically review each trade to understand whether the success was due to skill, luck, or favourable market conditions.
- Stick to Position Sizing Rules: Regardless of recent success, maintain consistent position sizes according to your risk management plan.
- Set Daily or Weekly Goals: Having specific goals can help you stay disciplined and avoid overextending after a winning streak.
- Boredom
During periods of low market activity or waiting for setups to align, traders might feel bored and make unnecessary trades to pass the time.
How to Deal with It:
- Create a Routine: Develop a trading routine that includes analysis, education, or other productive activities during slow periods.
- Practice Patience: Remind yourself that successful trading often involves waiting for high-probability setups rather than trading for the sake of it.
- Engage in Non-Trading Activities: Step away from the screens and engage in other activities to refresh your mind and avoid trading out of boredom.
- Reacting to News and Market Noise
Sudden news or rumours can lead to impulsive trading decisions as traders react without fully assessing the situation.
How to Deal with It:
- Avoid Knee-Jerk Reactions: Take time to analyze the news and its potential impact on the market before making any trades.
- Use a News Filter: Set up alerts or filters to focus only on news that significantly affects your trading instruments, ignoring minor or irrelevant noise.
- Incorporate News Analysis into Your Strategy: If news trading is part of your strategy, ensure its structured and based on clear criteria rather than impulsive decisions.
- Chasing Losses
After a losing trade, a trader may chase the market to try and quickly recover losses by entering new trades without proper analysis.
How to Deal with It:
- Implement a Cool-Down Period: Before placing new trades take a short break and make yourself comfortable. This is usually referred to as cool-down period.
- Reframe Your Mind-set: Understand that losses are part of trading. Focus on the bigger picture rather than trying to recover individual losses immediately.
- Set Loss Limits: Establish daily, weekly, or monthly loss limits to prevent yourself from chasing losses beyond a predetermined point.
- High Market Volatility
Rapid market movements can create a sense of urgency, leading traders to enter more trades to capitalize on the volatility.
How to Deal with It:
- Adjust Your Strategy: Tailor your trading strategy to account for increased volatility, possibly reducing position sizes or widening stop-loss levels.
- Focus on High-Probability Setups: Avoid the temptation to trade every movement. Instead, concentrate on setups that align with your strategy and offer the best risk-reward ratio.
- Stay Calm and Collected: Practice stress management techniques, such as deep breathing or mindfulness, to maintain focus during volatile markets.
- Peer Pressure
Being part of trading communities or groups where others are frequently discussing their trades can pressure a trader into taking more trades to keep up.
How to Deal with It:
- Trade Independently: Focus on your own trading rather than that of others. Remember that everyone has different strategies and risk tolerances.
- Limit Group Interactions during Trading Hours: Engage with trading communities outside of active trading hours to reduce the influence of peer pressure on your decisions.
- Cultivate a Strong Mind-set: Build confidence in your own trading plan and trust that your decisions are based on sound analysis rather than external influences.
1.1. Trading Psychology-Introduction
Psychology is pivotal in trading because the financial markets are not only analysed with profitable fundamentals but also by the feelings and behaviours of dealers. Dealers are prone to cognitive impulses similar as overconfidence, loss aversion, and evidence bias. Being apprehensive of and managing these impulses through a strong cerebral frame can lead to more accurate and unprejudiced decision.
Cerebral strength helps dealers view miscalculations and losses as learning openings rather than failures. This mind set fosters nonstop enhancement and development of better trading chops. In this course you’ll learn how to know unwanted passions getting in your way of trading, damaging your judgement. Also this course covers important strategies and threat operation ways to avoid crimes that dealers constantly make.
What’s Trading Psychology??
Trading psychology refers to the feelings and internal state that dealers witness while engaging in the financial trading. It encompasses the behaviours, and emotional responses that dealer’s exhibit, which can significantly impact their trading opinions and overall performance.
1.2. Significance of Trading Psychology
There are some crucial reasons why psychology is important in trading
-
Decision Making
Decision making feelings like fear and rapacity can significantly impact decision making processes. Effective trading requires making rational, objective opinions grounded on analysis rather than emotional responses.
Illustration
The decision of a dealer can have a profound impact on their trading issues. Here is an illustration that illustrates how a dealer’s mental state and decision making process can affect their trading
- Ajay is a dealer who has a well-defined trading strategy grounded on specialized analysis. His strategy involves setting stop loss orders to limit losses and taking gains at predefined situations. One day, there’s unanticipated news that causes significant request volatility.
- The price of the stock that Ajay is trading drops fleetly, approaching the stop loss position. Ajay feels a swell of fear as the price drops snappily rather than letting the stop loss order execute as planned, Ajay manually closes the trade to avoid further implicit losses.
- The stock price soon stabilizes and rebounds sprucely, recovering all its losses and moving towards the original profit target. By letting fear mandate the decision, Ajay exits the trade precociously, missing out on the implicit recovery and gains.
- Later, the same stock starts to rise steadily, and Ajay feels confident that it’ll continue to climb. Ajay decides to ignore the profit taking strategy and keeps holding the position, hoping for indeed greater earnings.
- The stock price hits a peak and also reverses, falling sprucely due to profit taking by other dealers. By succumbing to rapacity, Ajay holds the position too long and fails to secure the gains that were originally available, ultimately performing in a lower gain or indeed a loss.
- In this illustration, Ajay’s wrong decision lead to two critical miscalculations ending a trade precociously to avoid perceived further losses, missing the eventual recovery and ignoring the predefined profit target in expedients of advanced earnings, performing in missed profit taking openings.
-
Threat operation (Risk Management)
Proper mind helps dealers cleave to their threat operation strategies. Emotional trading frequently leads to overleveraging or taking on further threat than planned, which can affect in significant losses. Threat operation is a critical element of trading psychology, as it helps dealers cover their capital and maintain long term success.
Illustration
Imagine you are a trader who has just experienced a significant loss on a trade. The market moved against your position rapidly, leading to a loss larger than you anticipated. This loss triggers a strong emotional reaction—anger, frustration, and fear of further losses. You feel an intense urge to “win back” what you lost by immediately placing another trade.
Psychological Risk: This situation is ripe for psychological risks like:
-
- Revenge Trading: The desire to quickly recoup losses can lead to impulsive decisions, often without proper analysis, increasing the risk of further losses.
- Overtrading: Emotional stress might push you to take on more trades than usual, often with poor setups, leading to higher exposure and more potential losses.
- Loss Aversion: The fear of losing more may cause you to exit trades prematurely, locking in small losses or preventing potential gains.
Risk Management Strategies:
Pause and Reflect:
-
- Step Back: Immediately after a significant loss, step away from your trading station. Take a break to allow your emotions to settle. This pause helps prevent impulsive decisions driven by emotion rather than logic.
- Breathing Exercises: Engage in deep breathing or mindfulness exercises to reduce stress and regain a calm state of mind. This helps in clearing your mind and preparing you to think more rationally.
Review the Trade:
-
- Objective Analysis: When you return, review the trade that led to the loss. Analyze what went wrong: Was it a failure in your strategy, an unexpected market event, or an emotional decision? Understanding the cause helps in learning and preventing similar mistakes in the future.
- Record Keeping: Document the trade in a journal, noting the reasons for the loss, your emotional state, and what you learned. This practice not only aids in reflection but also serves as a reference for future trades.
Set Clear Rules:
-
- Loss Limits: Establish a maximum daily loss limit. If this limit is reached, stop trading for the day. This rule prevents the emotional spiral of trying to recover losses immediately, which often leads to more significant losses.
- Cool-Off Period: After a loss, enforce a mandatory cool-off period before placing any new trades. This time allows you to reset emotionally and ensures that any new trades are based on your strategy, not emotional reactions.
Focus on the Process, Not the Outcome:
-
- Detachment from Results: Cultivate a mind-set that focuses on executing your strategy correctly, regardless of the outcome of any single trade. Understand that losses are a natural part of trading and that sticking to a disciplined process is what leads to long-term success.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward yourself not just for winning trades, but for making disciplined decisions, even if the trade ends in a loss. This reinforces good habits and reduces the emotional impact of losses.
Seek Support:
-
- Mentorship or Community: Engage with a mentor or trading community where you can discuss your emotions and experiences. Sharing your challenges can provide perspective and support, helping you manage stress and stay grounded.
- Professional Help: If emotional reactions are consistently overwhelming and impacting your performance, consider consulting with a psychologist or counsellor specializing in trading psychology or stress management.
-
Consistency:
Successful trading requires consistency in executing strategies. Emotional control and psychological discipline ensure that traders follow their plans and do not deviate due to short-term market fluctuations. Consistency in trading psychology refers to the disciplined execution of a trading plan or strategy without being swayed by emotional impulses or short-term market fluctuations.
Example
A trader named Amit has developed a technical trading strategy based on moving averages and RSI (Relative Strength Index) indicators. His strategy includes the following rules:
- Entry Rule: Buy when the price crosses above the 50day moving average and the RSI is above 30.
- Exit Rule: Sell when the price crosses below the 50day moving average or the RSI exceeds 70.
- Position Sizing: Risk 2% of his trading capital on each trade.
- Stop Loss Orders: Set stop loss orders to limit potential losses to 2% of the trade’s value.
Amit has ₹20,000 in his trading account. He identifies a stock currently priced at ₹50 that meets his entry criteria.
Trade Execution:
-
- Entry Point: Amit buys 200 shares of the stock at ₹50 (2% risk on a ₹20,000 account means he can risk ₹400 on this trade).
- Stop Loss Order: He sets a stop loss order at ₹48 to limit his potential loss to ₹400 (200 shares x ₹2 loss per share).
Adhering to the Plan:
After purchasing the stock, the price drops slightly to ₹49, making Amit anxious. Despite his anxiety, Amit does not deviate from his strategy and keeps the trade open, adhering to his stop loss level. The stock price eventually rises to ₹55. Amit monitors the trade, and the RSI starts approaching 70. When the RSI hits 70 and the price is still above the 50day moving average, Amit decides to exit the trade, consistent with his strategy.
Outcome:
-
- Amit sells his 200 shares at ₹55
- Profit Calculation: He makes a profit of ₹1,000 (200 shares x ₹5 gain per share).
Amit follows the same consistent approach on his next trade. He identifies another stock meeting his entry criteria. Buys the stock, sets the stop loss, and exits based on his predetermined rules.
-
Stress Handling:
Trading can be stressful, especially during periods of high volatility or unexpected losses. Effective stress management through psychological resilience can help traders maintain focus and make sound decisions under pressure. Handling stress effectively is a crucial aspect of trading psychology, as it helps traders make sound decisions even under pressure.
Example
A trader named Shruti follows a swing trading strategy, focusing on holding positions for several days to weeks. Shruti has a trading account with ₹100,000 and typically risks 1% per trade. The market experiences sudden and extreme volatility due to unexpected geopolitical events. Shruti has several open positions, and the market’s rapid movements put her under significant stress.
Stress Management Techniques:
- Preparation and Planning: Before the volatility hit, Shruti had already established clear entry and exit points for each trade, including stop loss and take profit levels. This preparation helps Shruti avoid making impulsive decisions during high stress periods.
- Taking a Step Back: As the market swings wildly, Shruti feels her stress levels rising. She notices her heart rate increasing and a sense of panic setting in. Shruti steps away from her trading desk for a few minutes to take deep breaths and clear her mind. This brief break helps her regain composure and reduces immediate stress.
- Following the Plan: One of Shruti’s trades reaches its stop loss level. Instead of panicking and adjusting the stop loss to avoid the loss, Shruti allows the stop loss order to execute as planned. By following her predetermined plan, Shruti limits her loss to 1% of her account, which is within her risk tolerance.
- Using Stress Relief Techniques: Shruti practices deep breathing exercises to calm her nerves. She inhales deeply for a count of four, holds for a count of four, and exhales slowly for a count of four. After a particularly stressful trading session, Shruti goes for a walk outside. Physical activity helps reduce her stress and clear her mind.
- Reviewing and Learning: Once the market stabilizes, Shruti reviews her trades and the decisions she made under stress. She notes what worked well and where she can improve. Shruti uses this analysis to refine her trading strategy and improve her stress management techniques for future volatile periods.
-
Overcoming Biases:
Traders are prone to cognitive biases such as overconfidence, loss aversion, and confirmation bias. Being aware of and managing these biases through a strong psychological framework can lead to more accurate and unbiased decision-making. Overcoming biases is a crucial aspect of trading psychology, as cognitive biases can significantly impair decision-making and lead to suboptimal trading outcomes.
a. Confirmation Bias
Traders tend to seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs and ignore information that contradicts them. For example a trader named Amit believes that a particular stock will rise because of favourable news. He focuses on positive news articles and ignores negative analysis. Amit might overlook important risks and hold onto the stock despite signs that the price is likely to drop.
Overcoming Strategy:
Amit decides to deliberately seek out and consider opposing viewpoints. He reads bearish analyses and factors them into his decision-making process. By considering all available information, Amit can make a more balanced and informed decision, reducing the impact of confirmation bias.
b. Loss Aversion
Traders tend to prefer avoiding losses rather than acquiring equivalent gains, often leading to holding losing positions too long. For example a trader named Sarah is holding a stock that has dropped in value. She is reluctant to sell it because selling would mean realizing a loss. Sarah might hold the losing position, hoping it will recover, potentially resulting in greater losses.
Overcoming Strategy:
Sarah sets strict stop loss orders before entering trades and adheres to them regardless of her emotions. She also reviews past trades to reinforce the importance of cutting losses early. By accepting losses as part of trading and sticking to predefined exit points, Sarah can limit her losses and improve her overall performance.
c. Overconfidence Bias
Traders overestimate their knowledge, skills, and the accuracy of their predictions, leading to excessive risk-taking. For example, John has had a series of successful trades and starts believing that he has exceptional trading skills. He begins to take larger positions without proper analysis. Overconfidence leads John to take on excessive risk, which can result in significant losses when the market moves against him.
Overcoming Strategy:
John keeps a trading journal where he records his trades, reasons for entering and exiting, and outcomes. He regularly reviews his journal to remain humble and aware of his limitations. By maintaining a realistic view of his abilities and consistently analyzing his performance, John can avoid overconfidence and manage risk more effectively.
d. Recency Bias
Traders give undue weight to recent events or performance, assuming that these are indicative of future outcomes. For Example Shruti experiences a strong bullish trend in the market and assumes it will continue indefinitely. She makes trades based on this assumption. Shruti might ignore broader market indicators or signs of an impending reversal, leading to losses when the trend changes.
Overcoming Strategy:
Shruti develops a comprehensive trading plan that includes analysis of long-term trends, historical data, and market fundamentals. She uses this plan to guide her decisions rather than relying solely on recent performance. By basing her trades on thorough analysis rather than recent events alone, Shruti can make more balanced decisions and avoid the pitfalls of recency bias.
6. Patience and Discipline:
Markets do not always present clear opportunities. A strong psychological foundation helps traders stay patient and disciplined, avoiding impulsive trades that do not fit their strategy. Patience and discipline are crucial traits in trading psychology, essential for long-term success.
Example
Shruti, a seasoned trader, identifies a stock with strong fundamentals but is currently facing short-term market turbulence. She believes in the stock’s long-term potential but recognizes that the market may not reflect its value immediately. Shruti does not rush into buying the stock immediately. Instead, she waits for a confirmation signal from her technical analysis indicators, such as a moving average crossover or a breakout from a key resistance level. Despite seeing the stock price fluctuating and sometimes dropping, Shruti avoids making impulsive decisions based on fear. She reminds herself of her research and the stock’s long-term potential. Shruti maintains her focus on long-term gains rather than getting distracted by short-term market noise. She plans to hold the stock for several months or even years until it reaches her target price.
7. Adapting to Market Conditions:
Markets are dynamic and constantly changing. Psychological flexibility allows traders to adapt their strategies as needed rather than rigidly sticking to a plan that may no longer be effective. Adapting to market conditions is a vital aspect of trading psychology, as markets are dynamic and can change rapidly due to various factors.
Example
- Ajay, who is an experienced trader, has been successfully trading a particular stock using a trend following strategy. However, he notices that the market environment has shifted from a trending phase to a range bound or sideways phase. Ajay observes that the stock is no longer showing strong directional movement.
- Instead, it is oscillating within a defined range, bouncing between support and resistance levels. He recognizes that his trend following strategy might not be effective in this new market condition. Understanding the need for a different approach, Ajay decides to switch to a range trading strategy.
- This involves buying near the support level and selling near the resistance level, capitalizing on the predictable price movements within the range. Ajay revises his trading plan to incorporate the new strategy. He defines new entry and exit points based on support and resistance levels and adjusts his risk management rules accordingly.
- Ajay keeps himself updated with market news and events that could impact the stock’s price movements. He is aware that the market could break out of the range at any time, and he is prepared to adapt again if necessary. Despite the strategy change, he remains disciplined in executing his new plan.
- He does not get tempted to revert to his trend following strategy until there is clear evidence that the market has resumed trending. By adapting to the new market conditions, he avoids losses that might have occurred if he had continued with his trend following strategy.
- His new range trading approach proves effective, allowing him to generate profits in the sideways market. When the market eventually breaks out of the range and resumes trending, Ajay is ready to switch back to his original strategy.
8. Learning from Mistakes:
Psychological strength helps traders view mistakes and losses as learning opportunities rather than failures. This mind-set fosters continuous improvement and development of better trading skills.
Example
- Shyam a novice trader, has experienced several losing trades due to impulsive decisions and a lack of a structured trading plan. He takes a step back to reflect on his recent trading performance.
- He reviews his trading journal, noting the reasons for each loss, such as entering trades without proper analysis, not setting stop loss orders, and exiting trades prematurely due to fear.
- By analyzing his trading history, he identifies a pattern of emotional trading. He realizes that he often makes impulsive decisions driven by market news or short-term price movements, leading to poor trade outcomes.
- Understanding the need for improvement, he decides to educate himself further. He reads books on trading psychology, attends webinars, and follows experienced traders to learn about effective trading strategies and risk management techniques.
- With new knowledge, Shyam creates a detailed trading plan that includes specific criteria for entering and exiting trades, risk management rules, and guidelines for maintaining emotional control. He commits to following this plan, strictly monitors his trades closely, adhering to his trading plan and avoiding impulsive decisions.
- He keeps a trading journal to document each trade, including the rationale behind it, the outcome, and any emotional responses experienced. By learning from his mistakes and making necessary adjustments, Shyam begins to see improvements in his trading performance.
- Over time, his ability to learn from past mistakes helps him develop into a more successful and confident trader. Trading is not about short-term gains but rather long-term success. A strong psychological approach helps traders maintain a long-term perspective, focusing on sustainable growth rather than quick wins.
1.3. Influence of Social Media on Trading Psychology
Social media plays a significant role in shaping trading psychology in various ways:
1. Information Overload and Rapid News Dissemination
Social media platforms provide real-time news updates, which can lead to immediate market reactions. False or speculative information can spread quickly, causing traders to make impulsive decisions based on inaccurate data.
2. Herd Behavior and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
Seeing many people talking about or trading a particular stock or asset can lead traders to follow the crowd without conducting their own research. The fear of missing out on potential profits can drive traders to make hasty decisions, often leading to buying high and selling low.
3. Confirmation Bias and Echo Chambers
Traders might follow accounts and join groups that align with their existing beliefs, reinforcing their biases. These environments can create a false sense of consensus, making traders overconfident in their decisions.
4. Emotional Impact and Stress
Seeing others’ successes or failures can heighten emotions, leading to stress and emotional trading. Comparing one’s performance to others can create undue pressure, impacting trading decisions negatively.
5. Market Sentiment Analysis
Some traders use social media sentiment as a tool to gauge market trends and sentiment, though this can be a double-edged sword as sentiment can be volatile and manipulated.
6. Influencers and Opinion Leaders
Well-known traders and financial influencers can significantly impact market movements through their opinions and predictions. Unscrupulous individuals can use their influence to artificially inflate the price of an asset before selling it off, leaving others with losses.
7. Educational Resources and Community Support
Social media provides access to a wealth of educational content and community support, helping traders improve their skills and knowledge. Engaging with other traders can provide valuable insights and different perspectives on trading strategies and market analysis.
Example of Social Media Influence on Trading Psychology
- A notable example of social media’s influence on trading psychology in India is the case of the GameStop (GME) short squeeze in early 2021, which had global repercussions, including in India.
- This event was fueled significantly by discussions and campaigns on social media platforms like Reddit, particularly in the subreddit r/WallStreetBets. The GameStop short squeeze drew massive global attention, including from Indian traders.
- The news spread rapidly across social media platforms, leading to heightened interest and participation from traders around the world.
- Indian retail investors, influenced by the social media buzz, started looking for similar opportunities in their local market.
- There was an increase in activity on Indian stock market forums and social media groups discussing potential “short squeeze” targets in India. Stocks like Reliance Communications, Suzlon Energy, and other highly shorted stocks in India saw a significant increase in trading volumes as traders tried to replicate the GameStop phenomenon locally.
- Social media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and local forums like Moneycontrol’s message board saw a spike in discussions and posts about these stocks, driving more retail participation.
- Many traders jumped on the bandwagon without thorough research, driven by the fear of missing out (FOMO) on potential high returns that were being talked about on social media.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) closely monitored the situation to ensure market stability and protect retail investors from potential market manipulation.
- Following the incident, there were increased efforts to educate investors about the risks of following social media trends blindly and the importance of making informed trading decisions.
1.4 Winning V/s Loosing Stripes
Winning and losing stripes are common sensations in trading, and they can significantly impact a dealer’s psychology and decision making process. Understanding how to manage these stripes is vital for long term success.
Winning stripes
A winning band in the stock request is a period during which a stock or index closes at an advanced price for consecutive trading sessions. However, it’s on a five day winning band, if a stock’s price increases for five consecutive days.
Impact on Psychology
- Overconfidence a series of successful trades can lead to overconfidence, making dealers believe they are invincible. This can affect in taking devilish risks and swinging from their trading plan.
- Complacency Dealers might come insouciant, neglecting thorough analysis and due assiduity, assuming their winning band will continue indefinitely.
- Increased trouble Appetite Buoyed by recent success, dealers may increase their position sizes, influence, or trade more constantly, exposing themselves to lower implicit losses.
Operation Strategies
- Stick to the Plan Maintain discipline by adhering to the original trading plan, including trouble operation rules.
- Review and Reflect Regularly review formerly trades to understand the reasons behind successes and ensure they were due to sound strategy rather than luck.
- Stay Humble Acknowledge that requests are changeable and that no dealer is vulnerable to losses. Staying rested helps maintain a balanced approach.
Losing stripes
- A losing band in the stock request is a period during which a stock or index closes at a lower price for consecutive trading sessions.
- However, it’s on a six day losing band, if a stock’s price diminishments for six consecutive days.
Impact on Psychology
- Loss Aversion passing losses can lead to a violent emotional response where dealers come excessively concentrated on avoiding further losses, constantly leading to poor decision.
- Fear and Hesitation after a series of losses, dealers may come fearful and reticent to take new positions, indeed if the setup is favourable.
- Revenge Trading to recoup losses snappily, dealers might engage in revenge trading, taking fallacious risks and swinging from their plan.
Operation Strategies
- Take a Break Stepping down from the request temporarily can help clear the mind and reduce emotional stress, allowing for a more objective reassessment.
- Anatomize misapprehensions Review losing trades to identify any common misapprehensions or areas for improvement. This helps in knowledge and avoiding similar pitfalls in the future.
- Focus on the Process Shift the focus from short term issues to following the trading process and strategy. Density in execution will eventually lead to better results.
1.5 Developing the Right Trader’s Mind set
Developing the right mind set is vital for successful trading. It involves cultivating internal habits and stations that can help you handle the emotional and cerebral challenges of trading.
- Self-Discipline and forbearance produce a comprehensive trading plan with clear rules and guidelines. Cleave to this plan constantly, indeed during changeable periods. Repel the appetite to make impulsive opinions rested on heartstrings or request noise. Stick to your strategy and avoid chasing the request.
- Emotional Control Learn to recognize and manage your heartstrings, analogous as fear, cupidity, and frustration. Emotional control is essential for making rational opinions. Understand that losses are part of trading. Develop inflexibility to handle setbacks without letting them affect your unborn opinions.
- Realistic prospects set realistic, attainable trading pretensions rather than aiming for unrealistic earnings. Understand that harmonious, small earnings are more sustainable than large, erratic earnings. Recognize that trading is a continuous knowledge trip. Anticipate to make misapprehensions and view them as learning openings rather than failures.
- Risk Management Use stop loss orders and position sizing to manage trouble effectively. Guarding your capital is vital for long term success. Diversify your investments to spread trouble.
- Continuous improvement Document your trades, including the explanation behind each decision and the outgrowth. Engage with other dealers, join trading communities, and seek feedback to gain new perspectives and perceptivity.
- Strictness be set to adapt your strategy rested on changing request conditions. Harshness is vital to navigating different request surroundings. Keep up with request news, trends, and developments. Continuous knowledge will help you stay ahead and make informed opinions.
- Confidence and Humility Confidence in your strategy and decision making process is important. Still, ensure that confidence doesn’t turn into overconfidence. Recognize that no strategy is wisecrack confirmation and that you can always meliorate. Stay humble and open to learning from others.
- Focus on the Process, Not the Outcome Focus on following your trading plan and strategy rather than obsessing over individual trade issues. Constantly applying your process will lead to better long term results. Don’t let a single trade’s outgrowth dictate your overall strategy or tone assessment. Base your evaluation on adherence to your plan and trouble operation.
1.6 The secret of successful Trader Psychology
The secret to successful dealer psychology lies in learning a combination of internal disciplines, emotional operation, and strategic thinking, also are vital rudiments that contribute to a successful trading mind set.
1. Tone awareness and Emotional Intelligence
Be alive of how heartstrings like fear, cupidity, and overconfidence impact your decision. Understanding your emotional triggers can help you manage them better. Develop ways to manage stress and maintain countenance. This might include mindfulness, contemplation, or simply taking breaks from trading to regain perspective.
2. Discipline and density
Develop a well-defined trading plan with clear rules and stick to it. Density in following your plan helps in managing trouble and avoiding impulsive opinions. Establish a trading routine that includes regular analysis, review of formerly trades, and drug for the trading day. Harmonious routines can help make discipline and reduce stress.
3. Risk Management
Implement strict threat operation rules, similar as using stop loss orders and limiting position sizes. Guarding your capital ensures you can continue trading over the long term. Understand your threat forbearance and acclimate your strategies consequently. Effective threat operation is pivotal for surviving and thriving in unpredictable requests.
4. Growth Mind set
Treat losses and miscalculations as learning openings rather than failures. Assaying what went wrong and making adaptations can ameliorate your trading chops. Stay curious and married to literacy. Regularly modernize your knowledge, upgrade your strategies, and seek feedback from others in the trading community.
5. Focus and neutrality
Don’t let the excitement of trading lead to overtrading. Stick to your strategy and avoid making trades grounded on feelings or request noise. Base your opinions on data and analysis rather than particular impulses or external pressures. Ideal decision helps in maintaining thickness and discipline.
6. Adaptability and tolerance
Develop adaptability to handle ages of loss without letting them affect your confidence or decision making process. Tolerance is crucial to staying for the right openings and not forcing trades. Focus on long term pretensions rather than short term earnings. Trading success frequently requires time and continuity.
7. Rigidity
Be willing to acclimatize your strategies grounded on changing request conditions. Inflexibility allows you to respond to new information and evolving request dynamics. Keep up with request trends, news, and developments to make informed opinions and acclimate your approach as demanded.
8. Awareness and Balance
Maintain a healthy work life balance to avoid collapse. Engaging in conditioning outside of trading helps in keeping a clear mind and reducing stress. Incorporate awareness ways to stay focused and calm during trading. Awareness helps in managing feelings and perfecting decision.
1.7 Becoming a Disciplined Trader
A disciplined trader is someone who constantly follows a well-defined trading plan, maintains emotional control, and adheres to established threat operation practices. Crucial
Characteristics of a Disciplined Trader
Adherence to a Trading Plan
A chastened Trader follows a detailed trading plan with specific strategies, entry and exit points, and threat operation rules. Sticks to the plan anyhow of request conditions or feelings.
Emotional Control Remains calm and composed indeed during unpredictable request conditions. Makes opinions grounded on analysis and strategy rather than feelings like fear or rapacity.
Risk Management tools stop loss orders to minimize implicit losses. Precisely sizes positions to align with threat forbearance and overall portfolio strategy. Avoids concentrating too important capital in a single asset or trade.
Nonstop literacy and enhancement Stays informed about request trends, new trading strategies, and fiscal news. Regularly reviews past trades to learn from miscalculations and successes. Adjusts strategies as demanded grounded on request conditions and particular experience.
Attestation and analysis
Maintains a detailed journal of all trades, including the explanation behind each trade, issues, and reflections. Regularly evaluates trading performance to identify areas for enhancement.
Tolerance and Discipline
Doesn’t force trades but delays for setups that meet predefined criteria. Executes trades according to plan without divagation.
Illustration
One well known illustration of a chastened dealer in India is Rakesh Jhunjhunwala, frequently appertained to as the” Warren Buffett of India.” Though he was more extensively known as an investor, his disciplined approach to trading and investing provides precious assignments for dealers. Jhunjhunwala was known for his long term investment strategies, sticking to his persuasions indeed during request volatility. He conducts thorough abecedarian analysis before making investment opinions. Rakesh Jhunjhunwala chastened approach to trading and investing has made him one of the most successful and reputed personality. His styles and gospel offer precious perceptivity for dealers and investors aiming to develop discipline and achieve long term success.
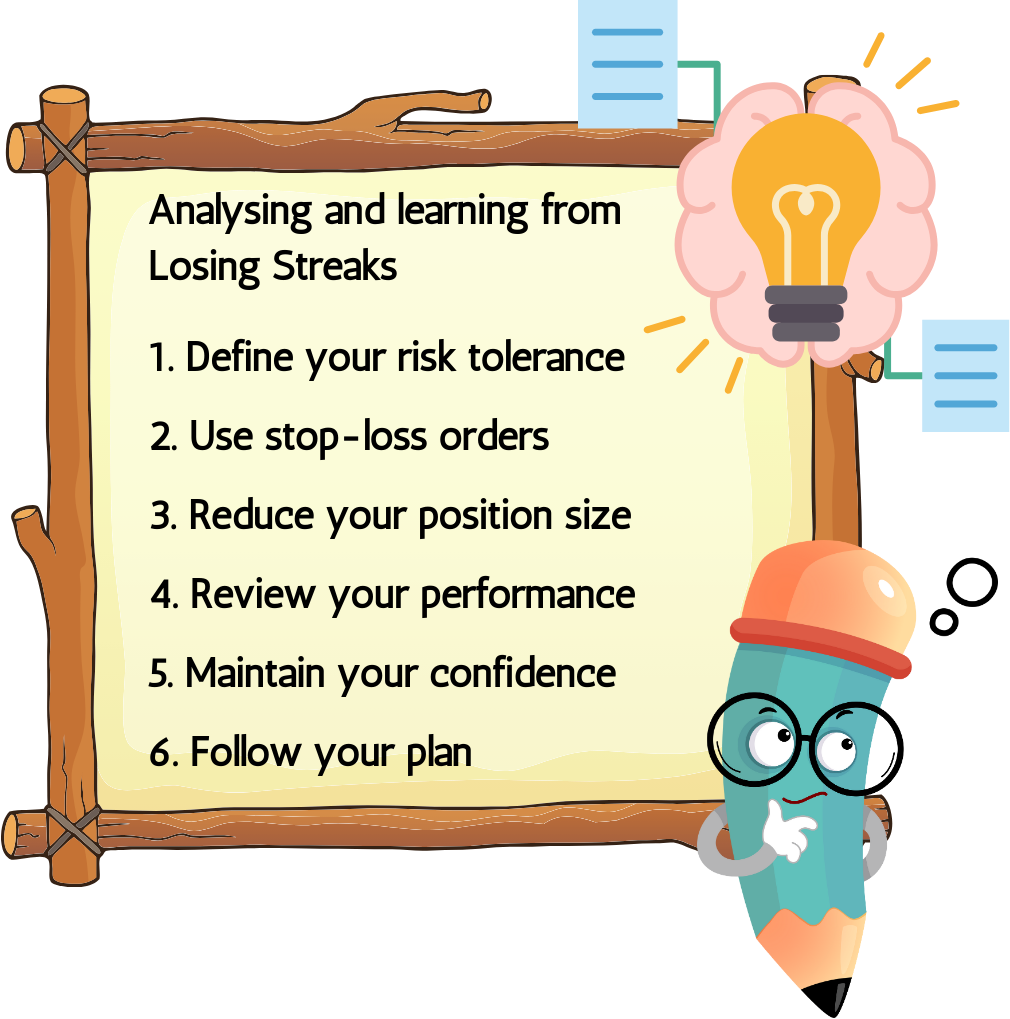
1.8 Analysing and learning from losing streaks
Analysing and learning from losing Streaks is pivotal for getting a successful and disciplined dealer.
1. Define your threat forbearance
Before you enter any trade, you should have a clear idea of how much you’re willing to risk and lose. This is your threat forbearance, and it depends on your trading style, pretensions, and personality. Your threat forbearance should be harmonious and realistic, not grounded on feelings. A common rule of thumb is to risk no further than 1 2 of your account balance per trade, but you can acclimate this according to your preferences.
2. Use stop loss orders
Stop loss orders are essential tools for guarding your capital and limiting your losses. They’re orders that automatically close your position at a destined price position, if the request moves against you. You should always use stop loss orders, and place them grounded on specialized analysis, not on arbitrary figures or wishful thinking. For illustration, you can use support and resistance situations, trend lines, moving pars, or pointers to set your stop loss orders.
3. Reduce your position size
One of the simplest and most effective ways to manage threat and position size during losing stripes is to reduce your exposure to the request. By trading lower quantities, you can reduce the impact of each loss on your account and your feelings. You can use a fixed chance or a fixed bone quantum to determine your position size, or you can use a threat price rate or a Kelly criterion to optimize it. The key is to be harmonious and disciplined, and not to overtrade or chase losses.
4. Review your performance
Losing stripes can also be openings to learn from your miscalculations and ameliorate your trading chops. You should review your performance regularly, and dissect your trades objectively. You should look for patterns, trends, strengths, and weakness in your and identify what works and what doesn’t. You should also keep a trading journal, where you record your entries, exits, reasons, feelings, and issues of each trade. This will help you track your progress, spot your crimes, and acclimate your strategy consequently.
5. Maintain your confidence
Losing streaks can also affect your confidence and motivation as a trader. You may start to doubt yourself, your system, or the market. You may become fearful, frustrated, or angry. You may lose sight of your long-term goals and vision. To avoid these negative effects, you should maintain your confidence and optimism during losing streaks. You should remind yourself of your past successes, your trading edge, and your potential. You should also practice self-care, such as taking breaks, exercising, meditating, or seeking support from others.
6. Follow your plan
Eventually, the most important tip on how to manage threat and position size during losing stripes is to follow your trading plan. Your trading plan is your roadmap to success, and it should include your pretensions, rules, criteria, styles, and pointers for trading. You should follow your trading plan rigorously, and not diverge from it grounded on feelings, impulses, or external influences. You should also review and modernize your trading plan periodically, and test it on different request conditions and scripts