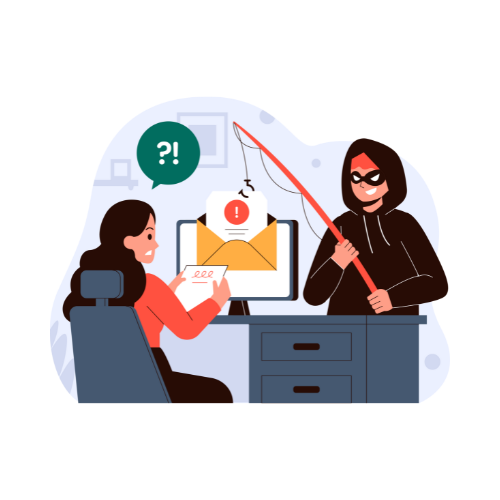
In the age of rapid technological advancement, India has witnessed a surge in cybercrimes, with one of the most alarming trends being the rise of “Digital Arrest” scams. These scams involve fraudsters posing as law enforcement officers to falsely accuse individuals of criminal activities and extort money or personal information from them. The phenomenon of digital arrest is not only a testament to the ingenuity of cybercriminals but also a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities that come with our increasing dependence on digital platforms. This blog aims to shed light on the concept of digital arrest, its modus operandi, recent incidents, the legal framework, and how individuals can protect themselves from falling victim to such scams.
What is Digital Arrest?
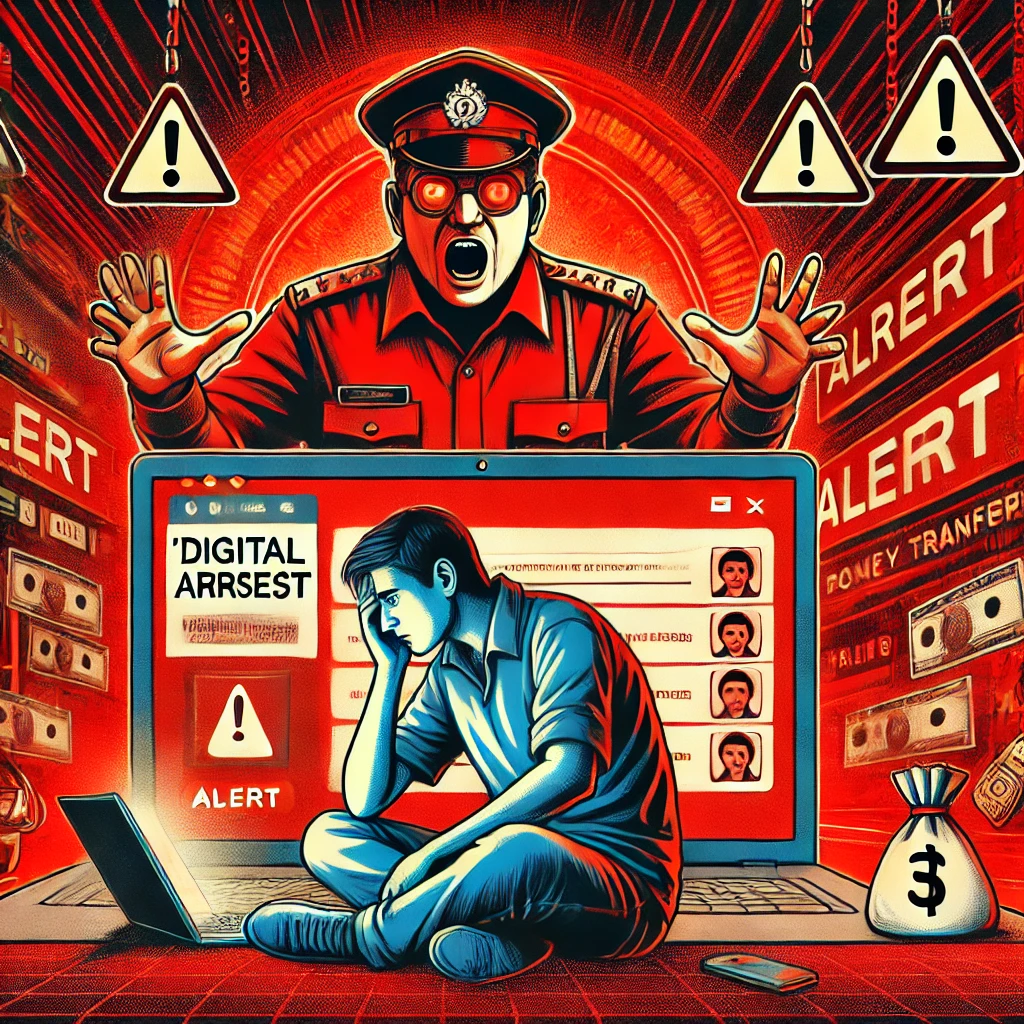

Digital arrest is a type of cybercrime where scammers impersonate law enforcement officials, such as police officers or CBI agents, to intimidate and deceive their victims. The fraudsters typically contact victims via phone calls, text messages, or social media, falsely accusing them of involvement in criminal activities like money laundering, tax evasion, or cybercrime. They create an atmosphere of fear by presenting themselves in agency uniforms and quoting legal provisions, ultimately threatening to arrest the victims unless they pay a specific sum of money.
The Anatomy of a Digital Arrest Scam
To understand the intricacies of digital arrest scams, it’s essential to delve into the modus operandi of these cybercriminals. The process can be broken down into several key stages:
- Research and Targeting: Cybercriminals often conduct extensive research to identify potential victims. They may gather personal information from social media profiles, public records, or data breaches. This information is used to tailor the scam to the victim’s specific circumstances, making it more convincing.
- Initiating Contact: The scam typically begins with a phone call, text message, or social media message from the fraudster posing as a law enforcement officer. The communication is often designed to create a sense of urgency and fear, pressuring the victim to comply quickly.
- False Accusations: The fraudster accuses the victim of a serious crime, such as money laundering, tax evasion, or involvement in a cybercrime. They may provide fabricated evidence or reference real legal provisions to make the accusations seem legitimate.
- Demands for Payment or Information: To avoid arrest or legal consequences, the victim is pressured to pay a fine or bribe. In some cases, the fraudster may also attempt to steal personal information, such as bank account details or passwords, which can be used for further fraudulent activities.
- Psychological Manipulation: The scam relies heavily on psychological manipulation. The fraudster may use threats, intimidation, and emotional appeals to manipulate the victim into compliance. They may also use sophisticated social engineering techniques to gain the victim’s trust.
Legal Framework and Enforcement
India has a robust legal framework to combat cybercrimes, including digital arrest scams. The primary legislation governing cybercrimes in India is the Information Technology Act, 2000, which provides legal recognition for electronic transactions and penalizes various forms of cybercrime. Additionally, the Indian Penal Code (IPC) includes provisions for offenses related to cheating, impersonation, and extortion, which can be applied to digital arrest scams.
Information Technology Act, 2000:
- Section 66D: This section deals with the punishment for cheating by personation using a computer resource. It prescribes a maximum punishment of three years of imprisonment and a fine.
- Section 67: This section addresses the punishment for publishing or transmitting obscene material in electronic form. While it may not directly apply to digital arrest scams, it highlights the broader scope of the Act in regulating online behaviour.
Indian Penal Code:
- Section 420: This section pertains to cheating and dishonestly inducing delivery of property. It prescribes a punishment of up to seven years of imprisonment and a fine.
- Section 416: This section defines cheating by personation, which involves deceitfully pretending to be someone else to commit fraud.
In addition to these legal provisions, law enforcement agencies in India, including the Cyber Crime Cells, have been actively working to combat cybercrimes. They have set up dedicated helplines and online portals for reporting cybercrimes, conducting awareness campaigns, and collaborating with international agencies to track and apprehend cybercriminals.
Challenges in Combating Digital Arrest Scams
While the legal framework and enforcement efforts are crucial in combating digital arrest scams, several challenges hinder the effectiveness of these measures:
- Anonymity of Cybercriminals: The anonymity provided by the internet makes it challenging to trace and apprehend cybercriminals. They often use sophisticated techniques to hide their identities and location, making it difficult for law enforcement agencies to track them.
- Cross-Border Nature of Cybercrimes: Many digital arrest scams are orchestrated by international cybercriminals, complicating the process of investigation and prosecution. The lack of uniform cybercrime laws and cooperation mechanisms between countries poses a significant challenge.
- Lack of Awareness: Despite the increasing prevalence of cybercrimes, many individuals and organizations remain unaware of the threats and preventive measures. This lack of awareness makes them more vulnerable to falling victim to digital arrest scams.
- Rapidly Evolving Tactics: Cybercriminals continuously evolve their tactics to evade detection and exploit new vulnerabilities. This dynamic nature of cybercrime requires law enforcement agencies to stay updated with the latest trends and technologies.
How to Protect Yourself
To protect yourself from digital arrest scams, consider the following tips:
- Verify Information: Never share personal information or financial details with anyone over the phone or online unless you are absolutely certain of their identity and the legitimacy of their request. Always verify the information provided by the caller or sender through official channels.
- Be Wary of Unfamiliar Numbers: Avoid answering calls from unknown numbers, especially those with foreign area codes. If you receive a suspicious call, do not engage in conversation and hang up immediately.
- Cross-Check Information: If you receive a suspicious call or message, try to verify the information with a trusted source, such as a government website or a known law enforcement agency. Do not rely solely on the information provided by the caller or sender.
- Stay Calm: Scammers rely on fear and panic to manipulate their victims. Stay calm and think rationally before taking any action. If you feel threatened or pressured, take a step back and seek advice from a trusted friend or family member.
- Report Suspicious Activities: If you suspect that you have been targeted by a digital arrest scam, report the incident to the authorities immediately. You can contact your local Cyber Crime Cell, file a complaint on the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal (https://cybercrime.gov.in/), or call the Cyber Crime Helpline at 155260.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest cybercrime trends and preventive measures. Participate in awareness programs and workshops conducted by law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity organizations.
- Use Technology Wisely: Implement cybersecurity best practices, such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping your software and devices updated. Use reputable antivirus and anti-malware software to protect your devices from malicious attacks.
Safeguarding Your Finances in a Digital Era
To navigate the digital financial landscape safely, it is essential to adopt robust cybersecurity practices and stay informed about potential threats. Here are some key strategies to safeguard your finances in a tech-driven era:
Strengthen Your Passwords and Authentication Methods
Passwords are the first line of defence against unauthorized access to your financial accounts. However, weak or easily guessable passwords can leave you vulnerable to attacks. Here are some tips for creating strong passwords and enhancing authentication methods:
- Use Complex Passwords: Create passwords that are at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid Common Passwords: Steer clear of using easily guessable passwords such as “123456,” “password,” or your birthdate.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Whenever possible, enable 2FA for your financial accounts. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your mobile device.
- Use a Password Manager: Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely. This can help you avoid the temptation of reusing passwords across multiple accounts.
Monitor Your Financial Accounts Regularly
Regularly monitoring your financial accounts is crucial for detecting and responding to unauthorized activities promptly. Here are some steps to help you stay vigilant:
- Set Up Account Alerts: Many financial institutions offer account alert services that notify you of suspicious activities, large transactions, or changes to your account settings. Enable these alerts to stay informed about any unusual activities.
- Review Statements and Transactions: Make it a habit to review your bank statements, credit card statements, and transaction history regularly. Report any unauthorized or suspicious transactions to your financial institution immediately.
- Check Your Credit Report: Periodically check your credit report to ensure that there are no unauthorized accounts or inquiries. In India, you can obtain a free credit report from credit bureaus such as CIBIL, Experian, or Equifax.
Protect Your Devices and Networks
The security of your devices and networks plays a crucial role in safeguarding your financial information. Here are some best practices to protect your digital assets:
- Install Security Software: Use reputable antivirus and anti-malware software to protect your devices from malicious attacks. Keep the software updated to ensure you have the latest security patches.
- Secure Your Wi-Fi Network: Use strong encryption (WPA3) and a complex password for your home Wi-Fi network. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for financial transactions, as they may be vulnerable to hacking.
- Update Your Devices: Regularly update the operating systems and software on your devices to patch security vulnerabilities. Enable automatic updates to ensure you receive the latest security fixes.
Be Cautious with Phishing Scams
Phishing scams are a common tactic used by cybercriminals to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information. These scams often involve fraudulent emails, messages, or websites that appear to be from legitimate sources. Here are some tips to protect yourself from phishing attacks:
- Verify the Source: Be cautious of unsolicited emails or messages that ask for personal or financial information. Verify the sender’s identity before clicking on links or providing any information.
- Look for Red Flags: Phishing emails often contain spelling and grammatical errors, urgent requests for action, or suspicious links. Be on the lookout for these red flags.
- Use Official Websites: When accessing financial services online, type the URL directly into your browser rather than clicking on links in emails or messages. This helps ensure you are visiting the legitimate website.
Educate Yourself About Cybersecurity
Knowledge is a powerful tool in safeguarding your finances. Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices by educating yourself and others:
- Attend Workshops and Webinars: Participate in cybersecurity workshops and webinars offered by financial institutions, cybersecurity firms, and educational organizations.
- Follow Trusted Sources: Follow reputable sources of cybersecurity information, such as the CyberSwachhta Kendra (Indian Computer Emergency Response Team) and cybersecurity blogs.
- Share Knowledge: Educate your family and friends about cybersecurity best practices. Encourage them to adopt secure habits to protect their financial information.
Utilize Secure Payment Methods
When making online transactions, choose secure payment methods to protect your financial information. Here are some options to consider:
- Use Credit Cards: Credit cards offer better fraud protection compared to debit cards. If unauthorized transactions occur, you can dispute them with your credit card issuer.
- Digital Wallets: Digital wallets, such as Paytm, Google Pay, and PhonePe, provide an additional layer of security by tokenizing your payment information. Use digital wallets for online purchases and contactless payments.
- Secure Payment Gateways: Ensure that the websites you use for online transactions are secure and use trusted payment gateways. Look for “https://” in the URL and a padlock icon in the browser address bar.
Backup Your Financial Data
Regularly backing up your financial data is essential for protecting against data loss due to cyberattacks, hardware failures, or other unexpected events. Here are some steps to ensure your data is safely backed up:
- Use External Drives: Backup important financial documents and records to external drives. Store these drives in a secure location.
- Cloud Storage: Utilize reputable cloud storage services to store encrypted copies of your financial data. This provides an additional layer of protection and accessibility.
- Regular Backup Schedule: Establish a regular backup schedule to ensure your data is consistently updated and protected.
Engage with Trusted Financial Institutions
Working with reputable and trusted financial institutions can significantly enhance the security of your financial transactions. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a financial institution:
- Reputation and Credibility: Choose financial institutions with a strong reputation for security and customer service. Research their cybersecurity measures and customer reviews.
- Security Features: Evaluate the security features offered by the financial institution, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and fraud detection systems.
- Customer Support: Ensure that the financial institution provides responsive customer support to address any security concerns or issues promptly.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies and Legislation
Regulatory bodies and legislation play a crucial role in safeguarding the digital financial landscape. In India, several regulatory authorities oversee financial security and implement measures to protect consumers:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
The RBI regulates and supervises the banking sector, ensuring that financial institutions adhere to cybersecurity standards and best practices. It issues guidelines on secure banking practices, digital payment security, and data protection.
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
SEBI oversees the securities market and ensures that stock exchanges, brokers, and other market participants implement robust cybersecurity measures. It issues regulations on data protection, cyber resilience, and fraud prevention.
- Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI)
IRDAI regulates the insurance sector and mandates that insurance companies implement cybersecurity measures to protect customer data and financial transactions. It also provides guidelines on data privacy and fraud prevention.
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
MeitY oversees policies and initiatives related to information technology and cybersecurity. It plays a crucial role in formulating guidelines and standards for data protection, digital payments, and cybersecurity infrastructure. MeitY’s initiatives, such as the Cyber Swachhta Kendra, aim to enhance cybersecurity awareness and provide resources for individuals and organizations to protect their digital assets.
- Personal Data Protection Bill
The Personal Data Protection Bill, proposed by the Government of India, aims to establish a robust framework for data protection and privacy. The bill outlines the responsibilities of data fiduciaries (organizations that process personal data) and provides guidelines for obtaining consent, data storage, and data processing. It also includes provisions for penalizing entities that fail to comply with data protection regulations.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Financial Security
While technology presents challenges in terms of cybersecurity and fraud, it also offers innovative solutions to enhance financial security. Here are some technological advancements that contribute to safeguarding your finances:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming the way financial institutions detect and prevent fraud. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time to identify suspicious patterns and anomalies. By leveraging AI and ML, financial institutions can implement advanced fraud detection systems that proactively monitor transactions and flag potential threats.
- Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, known for its association with cryptocurrencies, offers significant potential for enhancing financial security. The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain makes it resistant to tampering and fraud. Financial institutions are exploring the use of blockchain for secure transactions, digital identity verification, and transparent record-keeping.
- Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, and iris scanning, provide an additional layer of security for financial transactions. These methods offer a more secure and convenient alternative to traditional passwords and PINs. Many banks and financial apps are incorporating biometric authentication to enhance the security of their services.
- Encryption and Tokenization
Encryption and tokenization are essential techniques for protecting sensitive financial data. Encryption converts data into a coded format that can only be accessed with a decryption key. Tokenization replaces sensitive data with unique identifiers (tokens) that have no exploitable value. These techniques help ensure that financial data remains secure during transmission and storage.
- Secure Mobile Banking
Mobile banking apps are incorporating advanced security features to protect users’ financial information. Features such as end-to-end encryption, secure login, and biometric authentication help safeguard mobile banking transactions. Additionally, many apps offer tools for managing and monitoring accounts, allowing users to stay informed about their financial activities.
Case Studies:
Case Study 1: Digital Wallet Security
Ravi, a tech-savvy individual, uses a digital wallet app for most of his daily transactions, including paying bills, transferring money, and shopping online. One day, Ravi receives a phishing email that appears to be from his digital wallet provider, asking him to verify his account details. Suspicious of the email’s legitimacy, Ravi decides to contact the digital wallet provider directly using the official customer support number. The provider confirms that the email is fraudulent and advises Ravi to delete it immediately. Thanks to Ravi’s cautious approach and awareness of phishing scams, he avoids falling victim to identity theft. He also enables two-factor authentication on his digital wallet app and regularly monitors his transactions for any unauthorized activities. By following best practices for digital security, Ravi ensures that his financial information remains protected.
Case Study 2: Fraud Detection Using AI
Meera is a small business owner who uses online banking to manage her company’s finances. One day, she notices an unusual transaction in her business account and immediately contacts her bank. The bank’s fraud detection system, powered by AI and machine learning, had already flagged the transaction as suspicious and temporarily froze the account to prevent further unauthorized activities. The bank’s fraud detection team conducts a thorough investigation and confirms that the transaction was indeed fraudulent. Meera’s prompt action and the bank’s advanced fraud detection system prevent significant financial losses and ensure the security of her business account.
Case Study 3: Biometric Authentication for Secure Transactions
Anjali, a frequent traveller, relies on her mobile banking app to manage her finances while on the go. To enhance the security of her transactions, she enables biometric authentication on her app, using fingerprint recognition for secure login. During a trip abroad, Anjali receives an alert about an attempted login to her account from an unrecognized device. Thanks to biometric authentication, the unauthorized attempt is blocked, and Anjali’s account remains secure. The incident highlights the importance of using advanced authentication methods to protect financial accounts, especially when traveling or using public networks.
Real-Life Examples of Digital Financial Security
In November 2024, a 77-year-old woman from South Mumbai was duped of ₹3.8 crore by scammers posing as law enforcement officers. The scammers kept her under “digital custody” for over a month, making it the longest recorded digital arrest case in India. The scam began with a WhatsApp call informing her that a parcel she allegedly sent to Taiwan had been intercepted, containing passports, clothing, and drugs. The scammers claimed her Aadhaar card details were used in the offense and transferred her call to a fake police officer. The woman was asked to download Skype and was instructed not to disconnect the call or tell anyone about the case. The scammers, posing as IPS officers, asked for her bank account details and requested her to transfer money into their accounts as part of the investigation. They promised to return the money if she was found innocent. Over the course of a month, the woman transferred a total of ₹3.8 crore.This case highlights the importance of being vigilant and cautious when receiving unexpected calls or messages, especially those involving legal or financial matters.
Conclusion
In a tech-driven era, the convenience and efficiency of digital financial tools come with new challenges and risks. Cybersecurity threats, identity theft, and digital fraud are significant concerns that require proactive measures to safeguard your finances. By adopting robust cybersecurity practices, staying informed about potential threats, and leveraging technological advancements, you can navigate the digital financial landscape securely. Remember to strengthen your passwords, monitor your financial accounts, protect your devices and networks, and be cautious with phishing scams. Educate yourself about cybersecurity, utilize secure payment methods, and back up your financial data regularly. Engaging with trusted financial institutions and staying informed about regulatory developments can further enhance your financial security. As technology continues to evolve, staying vigilant and adopting a proactive approach to digital financial security is essential. By taking these steps, you can enjoy the benefits of the digital financial landscape while protecting your hard-earned money and securing your financial future.