- Study
- Slides
- Videos
6.1 Call And Put Option Meaning
- Call option gives the option holder(buyer) the right to buy the underlying asset at a particular price which is fixed(strike) for that particular time frame (expiration date).
- Put options give the right in the hands of the buyer to sell the underlying security by a particular date for the strike price, but he is not obligated to do so.
- A call option allows buying option, whereas Put option allows selling option.
- Profit is earned in a call option when the asset increases its price and when you are assuming a bullish trend. Profit is earned in the market for put options when you are assuming a bearish trend i.e. when the value of the underlying increases the call option earns profit whereas when the value of underlying decreases put option earns a profit.
- The potential gain in case of a call option is unlimited, but such gain is limited in the put option.
- In the call option, the investor looks for the rise in prices of the security. Conversely, in the put option the investor expects stock prices to go down.
- Buying a call option means the buyer needs to pay a premium to the seller. No margin is necessary However selling a put option requires the seller to deposit margin money with the stock exchange.
Some similar aspects are there in the two investments like both acts as an agreement between the buyer and seller in the financial market, where time works as an essence of the contract, i.e. the option needs to be exercised before the time expires. Moreover, the losses in both the cases are limited to the amount paid on premium.
Call And Put Option How Do They Work?
|
Underlying Asset’s Price |
What Is To Be Done? |
|
Probability of Increasing |
Buy Call Option Or Sell A Put Option |
|
Probability of Decreasing |
Buy Put Option Or Sell A Call Option |
6.2 Difference Between Call & Put Option
|
POINT OF DIFFERNECE |
CALL OPTION |
PUT OPTION |
|
Buyer Of The Option |
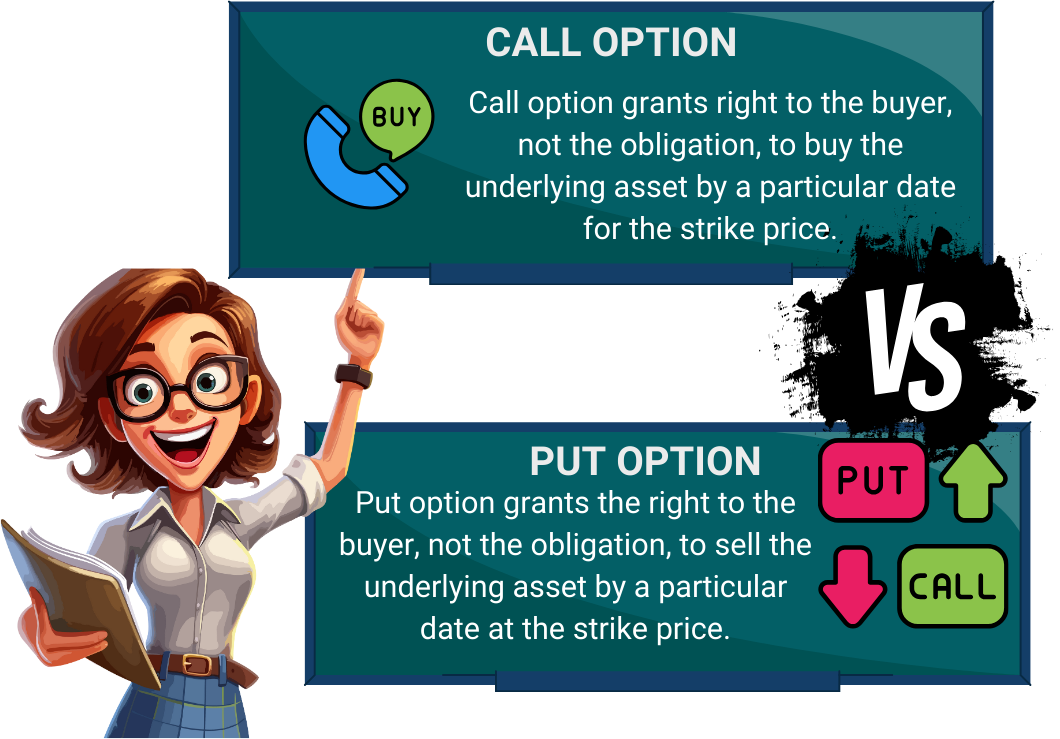
Call option grants right to the buyer, not the obligation, to buy the underlying asset by a particular date for the strike price. |
Put option grants the right to the buyer, not the obligation, to sell the underlying asset by a particular date at the strike price. |
|
Seller Of The Option |
Seller is obligated to sell the underlying asset to the option holder if the option is exercised |
Seller of put option is obligated to buy the underlying asset from the option holder if the option is exercised |
|
Value |
The value increases as the value of the underlying asset increases |
The value decreases as the value of underlying asset increases |
|
What It Allows? |
Buying of stock |
Selling of stock |
|
Relationship With Stock Market |
Direct |
Inverse |
|
Potential Gain |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
Investor Looks For |
Price Rise |
Fall in prices |
6.3 Risk & Rewards Related to Call And Put Options
We have tabulated a simple list of how the risks and rewards will work out if you are trading in call and put options: –
|
Parameters |
Call Option Buyer |
Call Option Seller |
Put Option Buyer |
Put Option Seller |
|
Maximum Gain |
Unlimited |
Premium Amount Received |
Strike Price – Premium Paid |
Premium Amount Received |
|
Maximum Profit |
Premium Paid |
Unlimited |
Premium Paid |
Strike Price – Premium |
|
Zero Profit – Zero Loss |
Strike Price + Premium Paid |
Strike Price + Premium Paid |
Strike Price + Premium Paid |
Strike Price + Premium Paid |
|
Ideal Action |
Exercise |
Expire |
Exercise |
Expire |
Now Let us deep dive into how the payoffs for each of these parameters will work: –
Situation 1: – If You Are a Buyer of Call Option
What Happens to Call Options on Expiry?
In call and put options, when you buy a call option, these are the three things that can happen during expiry:
- Market Price > Strike Price = In The Money Call Option = Gains
- Market Price < Strike Price = Out of The Money Call Option = Losses
- Market Price = Strike Price = At The Money Call Option = Break Even
Situation 2: – If You Are A Seller of a Call Option
What Happens to Call Options on Expiry?
When you sell a call option these are the three likely scenarios that can occur when selling a call option: –
- Market Price > Strike Price = In The Money Call Option = Loss
- Market Price < Strike Price = Out of The Money Call Option = Gains
- Market Price = Strike Price = At The Money Call Option = Profit In the Form Of Premium
If you wish to know more about call option payoffs and how to the work you can read about call option basics.
Situation 3: – If You Are a Buyer of Put Option
What Happens to Call Options on Expiry?
- Market Price > Strike Price = Out Of The Money Put Option = Loss
- Market Price < Strike Price = In The Money Put Option = Gains
- Market Price = Strike Price = At The Money Put Option = Loss In The Form of premium paid
Situation 4: – If You Are a Seller of Put Option
- Market Price > Strike Price = Out Of The Money Put Option = Gains
- Market Price < Strike Price = In The Money Put Option = Losses
- Market Price = Strike Price = At The Money Put Option = Profit In The Form of Premium
If you wish to know more about call option payoffs and how to the work you can read about put option basics.
6.4 Example to explain the difference between call option and put option
Let us say Naman purchased a put option for selling 20 shares of a company at Rs. 5,000 each after two months. Ritesh has entered the contract with a call option of buying the shares at the same price, volume, and time frame.
However, if the price increases to Rs.7,000, Naman would make a loss. However, he would still have to sell the shares for much less than their market worth. This is when purchasing a call option helps. If the price of a share appreciates, your investment works.
Now, let us look at how it works if the price of the share falls to Rs.4,500. Now, purchasing the share at INR 5,000 would make it a bad trade for Ritesh. So, being a call buyer, he can choose to walk out. He doesn’t have to buy the stocks underlying the contract. When he walks out, he is not charged a penalty, but his loss is the premium he paid.
If he chooses to buy the shares nonetheless, it’s a profit for the put option buyer. He can sell the shares at a higher price and use the difference for his next investment, profits, liquidity, etc.
For your call option to be profitable, the shares you purchased the contract for have to appreciate in the given time frame, so that you can trade them in the market openly and make profits.
For your put option to have gains, the shares you have to sell must depreciate in price, so that if the buyer goes through with his trade, you have to sell the shares at higher prices than what is currently prevailing in the market. You can then use the remainder to buy the shares back for a lesser sum.