- Study
- Slides
- Videos
2.1 What is Options scalping All About??
- Options scalping is a trading strategy where traders aim to profit from short-term price movements or changes in volatility in options contracts. Unlike traditional options trading, which may involve holding positions for days or weeks, options scalping involves making rapid trades with the goal of generating quick profits. Here’s a closer look at what options scalping entails:
- Options scalping typically focuses on very short timeframes, often minutes or even seconds. Traders enter and exit positions swiftly, aiming to capitalize on immediate price movements or shifts in options prices due to changes in volatility. Scalpers look for options contracts that are experiencing rapid price changes or fluctuations in implied volatility. They may use technical analysis indicators or real-time market data to identify short-term opportunities for profit. Options scalping often involves a high volume of trades executed within a short period. Scalpers rely on advanced trading platforms and technology to execute orders quickly and efficiently, taking advantage of small price differentials between bid and ask prices.
- Scalpers prefer options contracts with high liquidity and tight bid-ask spreads, as this allows for faster order execution and minimizes trading costs. They may focus on heavily traded options on popular underlying assets. Options scalping is primarily an intraday trading strategy, with positions typically being opened and closed within the same trading session. Scalpers avoid holding options contracts overnight to minimize exposure to overnight risks such as changes in market sentiment or unexpected news events. While options scalping can be profitable, it also comes with inherent risks.
- Scalpers employ risk management techniques such as setting stop-loss orders, position sizing, and maintaining strict discipline with regard to entry and exit criteria to protect capital and minimize losses. Options scalping often involves trading volatility itself, as changes in implied volatility can significantly impact options prices. Scalpers may use strategies such as straddles, strangles, or iron condors to profit from expected changes in volatility levels. Options scalping may involve more complex options trading strategies beyond simple buying or selling of individual options contracts. Traders may also use combinations of options positions, such as spreads or butterflies, to structure trades that are designed to profit from specific market conditions or price movements.
- Overall, options scalping requires a high level of skill, discipline, and proficiency in options trading mechanics. It’s a fast-paced and demanding strategy that can be rewarding for traders who are able to execute it effectively, but it also carries risks and may not be suitable for all investors.
2.2 Example of Options Scalping:
Suppose Amit is trading options on Company stock ABC, which is currently trading at ₹100 per share. Amit notices that the market is volatile to an earnings announcement scheduled for later in the day. Amit believes that the stock price will go up in the morning before dropping back down after the earnings announcement. As a scalper, Amit decides to take advantage of this short-term price movement. He purchases a call option with a strike price of ₹102, expiring in one hour, for ₹1 per contract. This means he has the right to buy Company ABC stock at ₹102 per share within the next hour.
Shortly after his purchase, the stock price indeed rises to ₹102 per share, as he had predicted. The value of his call option increases to ₹2 per contract. Recognising the opportunity to profit, he sells his call option for ₹2, doubling his amount in a short period. In this example, Amit successfully executed a scalping trade by identifying a short-term price movement, buying an option to capitalize on it, and selling the option quickly for a profit before the price reversed.
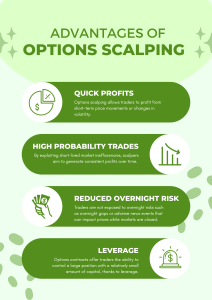
2.3 Advantages of Options Scalping
Options scalping offers several advantages for traders who are skilled at executing this trading strategy effectively:
- Quick Profits: Options scalping allows traders to profit from short-term price movements or changes in volatility, often within minutes or even seconds. Scalpers aim to capture small price discrepancies or fluctuations in options prices, generating rapid profits on each trade.
- High Probability Trades: Scalping options can offer high-probability trading opportunities, as traders focus on short-term price movements or shifts in volatility that are often more predictable than longer-term trends. By exploiting short-lived market inefficiencies, scalpers aim to generate consistent profits over time.
- Reduced Overnight Risk: Since options scalping typically involves closing out all positions by the end of the trading day, traders are not exposed to overnight risks such as overnight gaps or adverse news events that can impact prices while markets are closed. This can help to reduce overall risk exposure and provide greater peace of mind for traders.
- Leverage: Options contracts offer traders the ability to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital, thanks to leverage. Scalpers can use leverage to amplify their potential profits on each trade, although it’s important to manage leverage carefully to avoid excessive risk.
- Flexibility: Options scalping can be applied to various market conditions and asset classes, including stocks, forex, commodities, and indices. Traders can use scalping strategies in different markets, such as trending markets, range-bound markets, or high-volatility environments.
- Diversification: Options scalping allows traders to diversify their trading activities across multiple assets, strike prices, and expiration dates. By spreading risk across different options contracts, traders can reduce their exposure to any single trade or market event.
- Lower Capital Requirements: Compared to other trading strategies that may require holding positions for longer periods or maintaining large capital reserves, options scalping can be executed with relatively low capital requirements. Scalpers can make use of margin accounts and leverage to maximize their trading potential without tying up significant amounts of capital.
- High Liquidity: Options markets tend to be highly liquid, especially for actively traded options on popular underlying assets. This high liquidity ensures that options scalpers can enter and exit positions quickly and efficiently, minimizing slippage and maximizing trading opportunities.
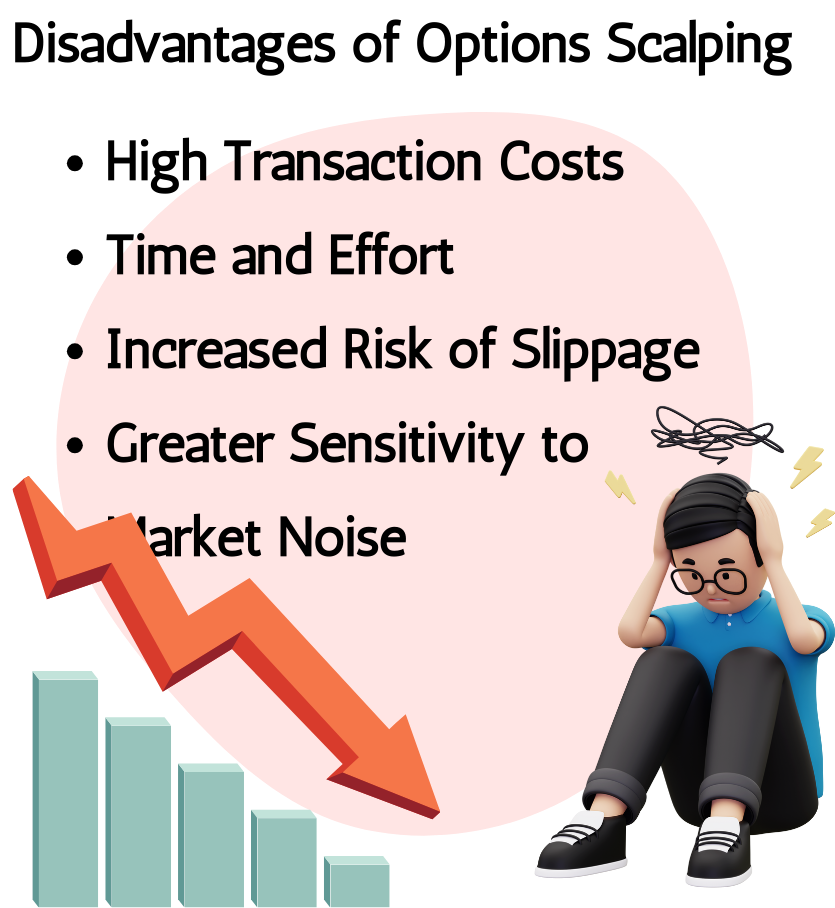
2.4 Disadvantages of Options Scalping
While options scalping can offer potential advantages, it also comes with certain disadvantages and risks that traders should be aware of:
- High Transaction Costs: Options scalping involves making a large number of trades within a short period, which can result in significant transaction costs, including commissions, fees, and bid-ask spreads. These costs can eat into profits, particularly for traders with smaller trading accounts.
- Time and Effort: Options scalping requires constant monitoring of the markets and rapid decision-making. Traders need to devote considerable time and effort to analyzing market conditions, identifying trading opportunities, and executing trades quickly. This can be mentally and emotionally demanding, leading to stress and burnout for some traders.
- Increased Risk of Slippage: Rapidly entering and exiting positions in options contracts can increase the risk of slippage, where trades are executed at a less favourable price than expected due to market volatility or liquidity constraints. Slippage can erode profits and impact overall trading performance.
- Greater Sensitivity to Market Noise: Options scalping focuses on short-term price movements and volatility, which can be influenced by market noise and random fluctuations. Traders need to distinguish between genuine trading signals and noise to avoid entering trades based on false signals, which can result in losses.
- Limited Profit Potential: While options scalping can generate quick profits on individual trades, the profit potential per trade is typically limited due to the small price differentials or fluctuations that scalpers target. Traders need to make numerous trades to accumulate significant profits, which requires consistency and discipline.
- Risk of Overtrading: The fast-paced nature of options scalping can lead to overtrading, where traders execute trades excessively and impulsively without proper analysis or justification. Overtrading can increase transaction costs, increase the risk of losses, and undermine overall trading performance.
- Dependency on Market Conditions: Options scalping strategies may be highly dependent on specific market conditions, such as high volatility or tight bid-ask spreads. When market conditions change, such as during periods of low volatility or illiquidity, options scalpers may struggle to find profitable trading opportunities.
- Difficulty in Scalability: Scaling up options scalping strategies to larger position sizes or higher frequency trading can be challenging due to liquidity constraints, market impact costs, and the risk of slippage. Traders need to carefully manage position sizes and trading frequency to maintain profitability as they scale up their operations.
2.5 Key Elements in Options Scalping
Options scalping is a trading strategy focused on profiting from short-term price movements or changes in volatility in options contracts. To effectively implement options scalping, traders need to consider several key elements:
- Market Analysis: Options scalpers begin by analyzing market conditions, including the underlying asset’s price action, volatility levels, and overall market sentiment. They use technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and market news to identify potential trading opportunities.
- Option Selection: Traders select options contracts that are liquid, have tight bid-ask spreads, and exhibit the desired level of volatility. They may focus on options with short expiration dates to capitalize on near-term price movements.
- Entry and Exit Criteria: Scalpers establish clear entry and exit criteria based on their analysis and trading strategy. Entry points may be based on technical indicators, price patterns, or changes in volatility, while exit points are typically determined by predefined profit targets or stop-loss levels.
- Risk Management: Effective risk management is essential in options scalping to protect capital and minimize losses. Scalpers use techniques such as position sizing, stop-loss orders, and portfolio diversification to manage risk exposure.
- Order Execution: Scalpers rely on fast and efficient order execution to capitalize on short-lived trading opportunities. They use direct market access (DMA) platforms and advanced trading tools to execute orders quickly and accurately.
- Liquidity: Liquidity is crucial in options scalping, as traders need to enter and exit positions without significant slippage. Scalpers focus on options contracts with high trading volume and tight bid-ask spreads to ensure liquidity.
- Volatility Trading: Options scalping often involves trading volatility itself, as changes in implied volatility can impact options prices. Scalpers may use strategies such as straddles, strangles, or iron condors to profit from expected changes in volatility levels.
- Adaptability: Markets are dynamic and constantly evolving, so options scalpers must be adaptable and able to adjust their strategies based on changing market conditions. This may involve modifying trading parameters, switching between bullish and bearish strategies, or exiting trades quickly if conditions change unfavourably.
- Technology and Tools: Options scalpers utilize advanced trading platforms, real-time market data, and trading tools such as options scanners and volatility indicators to identify trading opportunities and execute trades efficiently.
- Discipline and Patience: Options scalping requires discipline and patience, as traders need to wait for the right trading setups and adhere to their trading plan rigorously. They avoid impulsive decisions and emotional trading, sticking to their predefined rules and strategies.
2.6 How Options Scalping Works??
Option scalping works by taking advantage of short-term price movements in options contracts to generate quick profits. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it typically operates:
- Identifying Tradable Assets: Scalpers look for assets with high liquidity and volatility, as these characteristics increase the likelihood of price movements that can be exploited for profit. Common underlying assets for options scalping include stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and indices.
- Analysing Market Conditions: Before initiating trades, scalpers analyse market conditions and trends using technical analysis tools and indicators. They look for short-term price patterns and momentum signals that suggest potential opportunities for quick profits.
- Selecting Options Contracts: Scalpers focus on short-term options contracts with expiration dates ranging from days to weeks. They typically prefer contracts with high trading volume and tight bid-ask spreads to ensure liquidity and minimize slippage.
- Entry and Exit Points: Scalpers identify precise entry and exit points based on their analysis of price action and technical indicators. They aim to enter positions at optimal prices and exit quickly with a profit before price reversals occur.
- Managing Positions: Once a position is opened, scalpers closely monitor market developments and adjust their positions accordingly. They may use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and trailing stops to protect profits as prices move in their favour.
- Executing Trades: Scalpers rely on fast and efficient execution to capitalize on short-term price movements. They often use advanced trading platforms that offer direct market access and low-latency execution to ensure timely order placement and execution.
- Risk Management: Risk management is a critical aspect of option scalping. Scalpers carefully manage position sizes, set strict stop-loss orders, and adhere to predefined risk-reward ratios to minimize losses and preserve capital.
- Continuous Monitoring: Option scalping requires constant monitoring of market conditions and positions throughout the trading session. Scalpers stay vigilant for new trading opportunities and react quickly to changing market dynamics to maximize profits and minimize risks.
Key Takeaways
- Options scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy aimed at profiting from small price movements in options contracts over very short time frames. Traders execute numerous trades throughout the day, targeting minimal price changes to accumulate small profits that add up.
- This method relies heavily on technical analysis, advanced trading platforms, and quick decision-making.
- While it offers the potential for quick gains, it involves significant risk, high transaction costs, and requires strong emotional control and robust risk management strategies. Option scalping requires constant monitoring of market conditions and positions throughout the trading session.