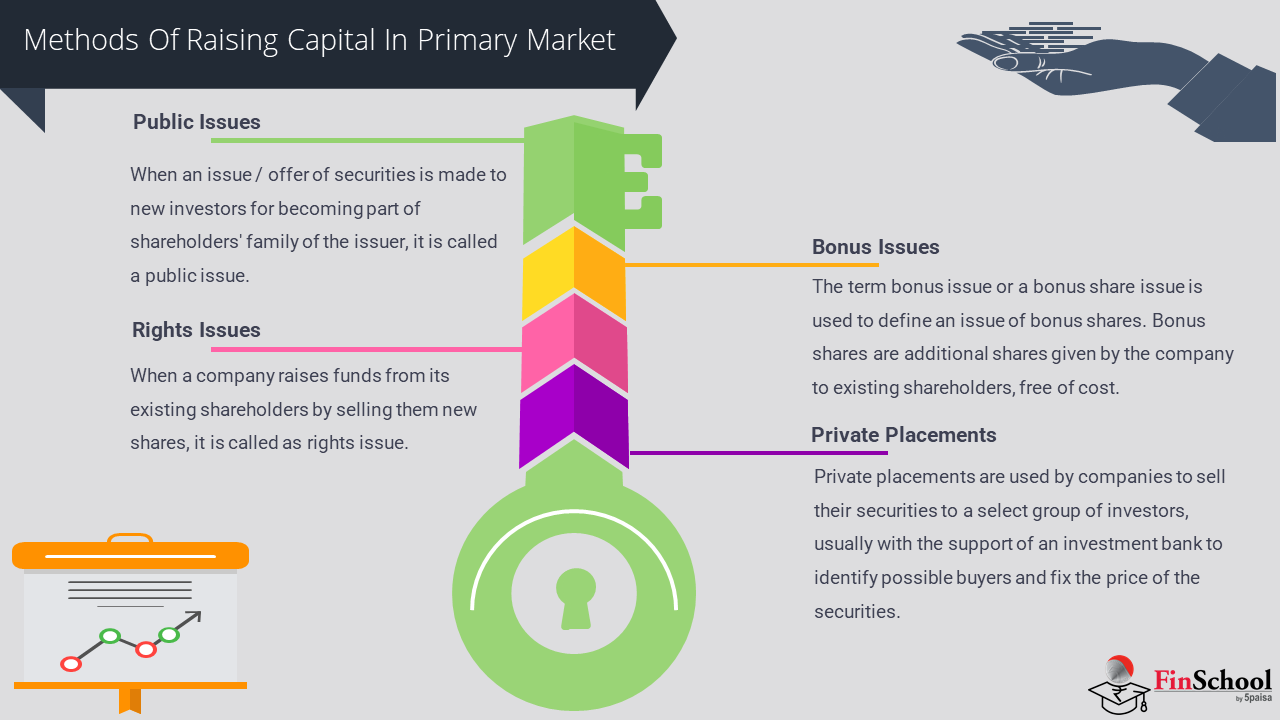
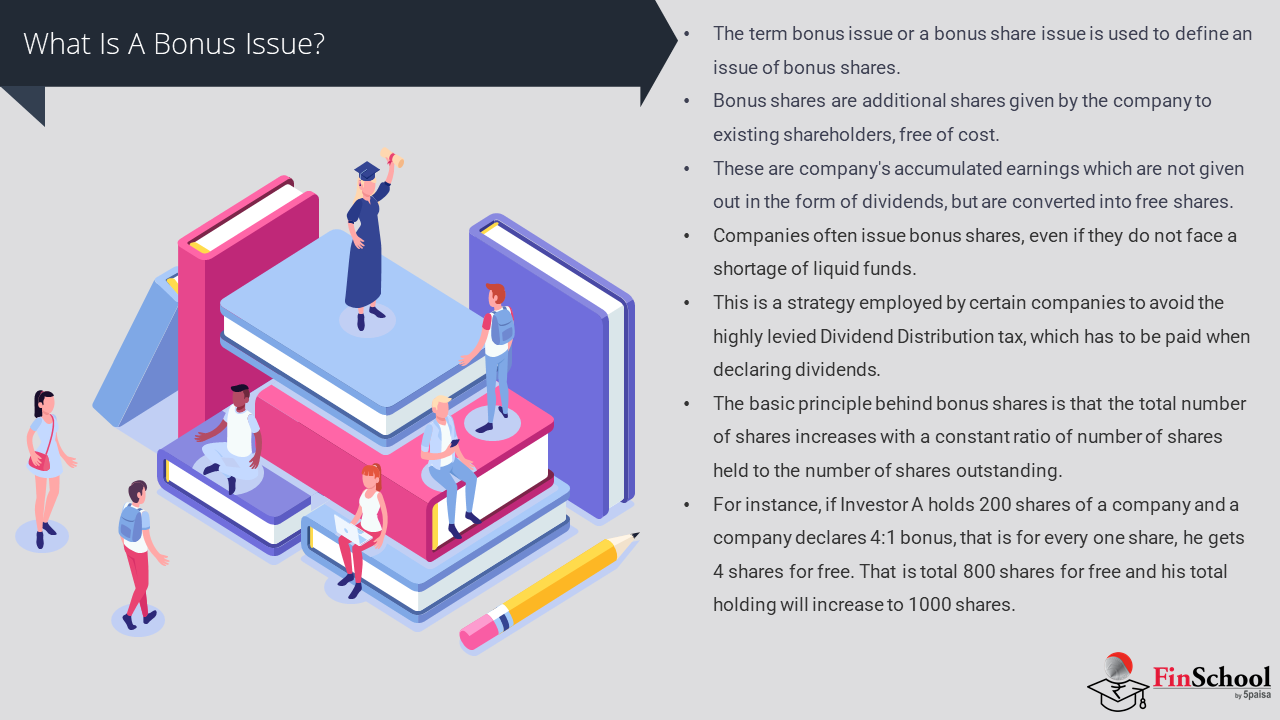
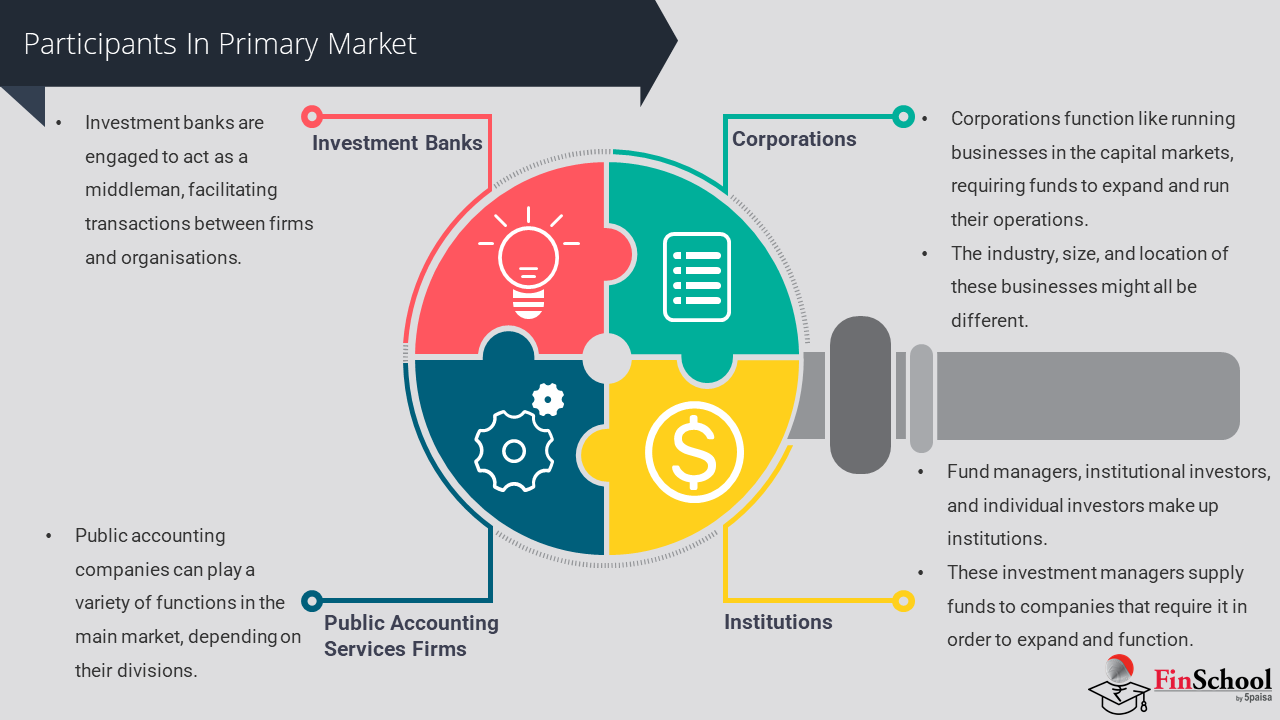
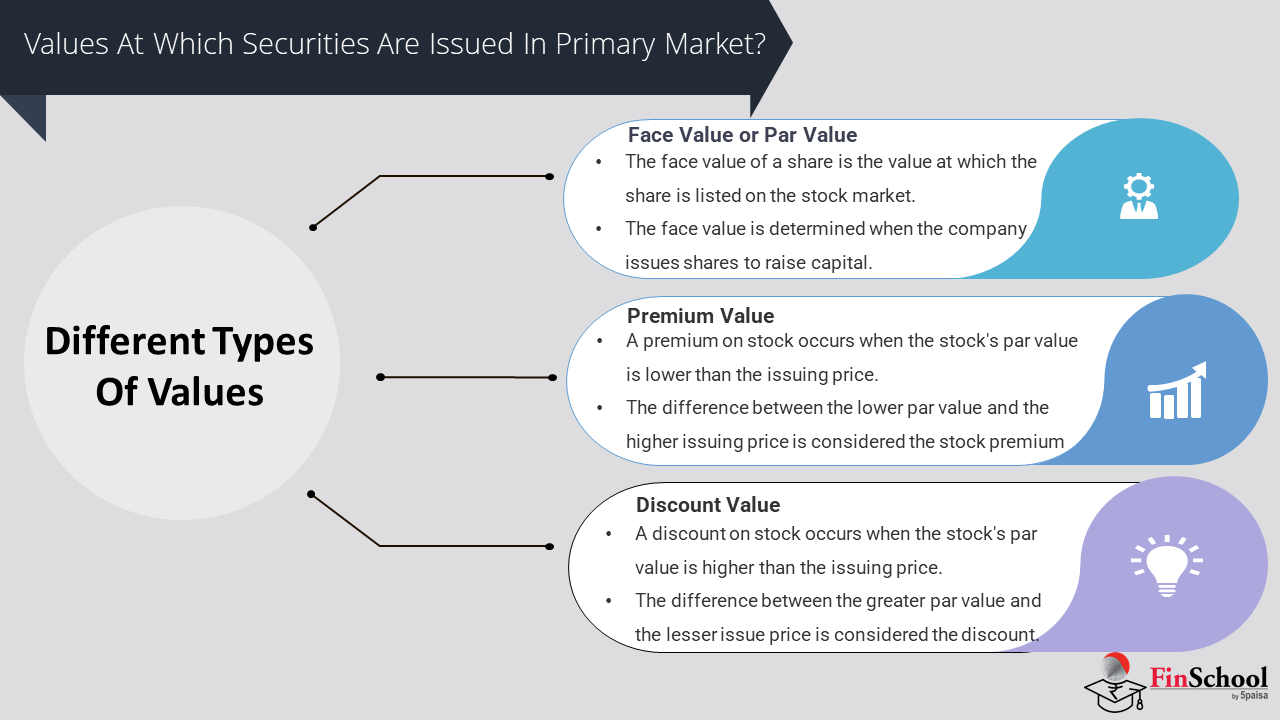
- Study
- Slides
- Videos
7.1.What are Volatile Stocks??
Volatile stocks are those that experience large price fluctuations over a short period. These fluctuations can occur due to various factors, including company news, earnings reports, market sentiment, economic data, or external events. Here are some characteristics of volatile stocks:
- Wide Price Swings: Volatile stocks often exhibit significant and rapid price movements, with prices fluctuating both upwards and downwards within a short timeframe.
- High Beta: Beta measures a stock’s volatility compared to the overall market. Volatile stocks typically have a high beta, meaning they tend to move more than the market average.
- High Trading Volume: Volatile stocks often have high trading volumes, as increased trading activity can contribute to price volatility.
- News Sensitivity: These stocks are highly sensitive to news and events related to the company, industry, or broader market.
- Low Liquidity: While high trading volume is common for volatile stocks, some may have low liquidity, which can exacerbate price movements and increase the risk of slippage.
- Speculative Interest: Volatile stocks often attract speculative traders and investors seeking to profit from short-term price movements. This speculative interest can contribute to increased volatility.
- High Risk and Reward: Investing in volatile stocks can offer the potential for high returns but also comes with high risk. The rapid price fluctuations can lead to significant gains or losses in a short period.
7.2. What is India VIX??
- India VIX, also known as the India Volatility Index, is a measure of market volatility. It is based on the implied volatility of the NIFTY 50 index options contracts traded on the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE). Implied volatility is a measure of the market’s expectation of future volatility of the underlying asset, derived from the prices of options contracts.
- India VIX provides investors and traders with an indication of the expected volatility in the Indian stock market over the next 30 days. Generally, higher values of India VIX indicate higher expected volatility, while lower values indicate lower expected volatility.
- It is often used by market participants to gauge the level of risk and uncertainty in the market and to make informed decisions regarding hedging or trading strategies.
- India VIX is calculated using the Black-Scholes model, which takes into account factors such as the current price of the NIFTY 50 index, the strike prices of NIFTY 50 options, the time to expiration, and the prevailing interest rates. The calculation results in a percentage value that represents the annualized expected volatility of the NIFTY 50 index over the next 30 days.
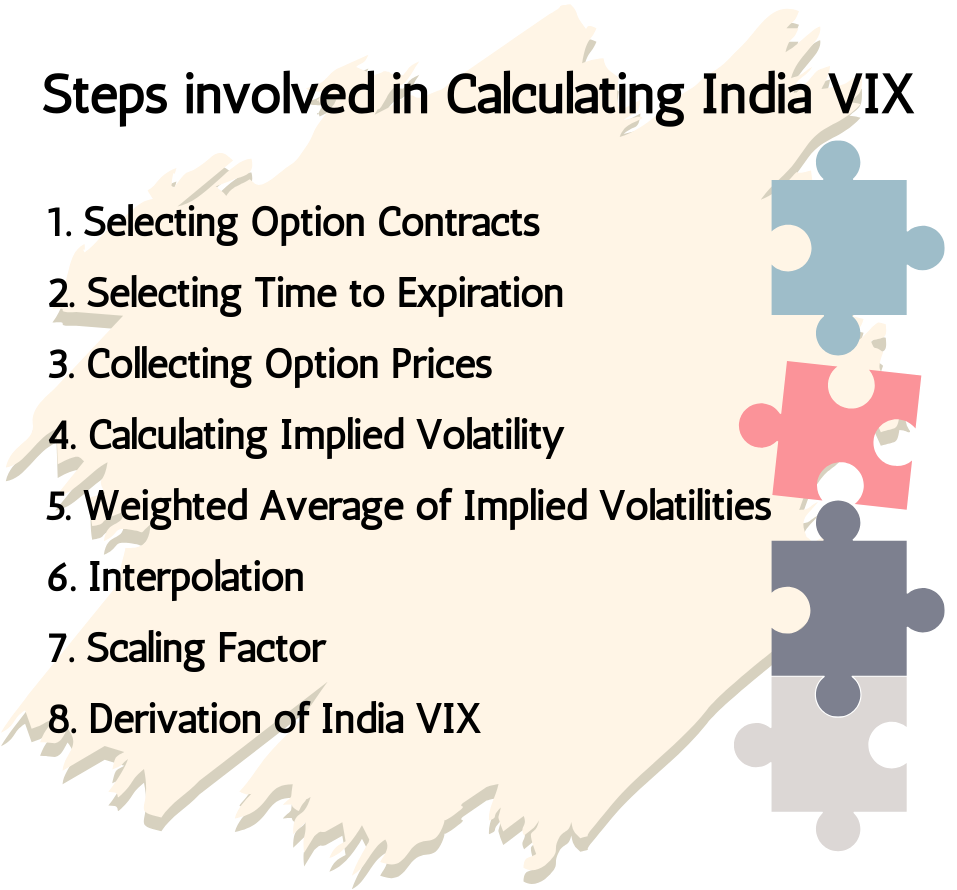
7.3. Steps involved in Calculating India VIX
Calculating the India VIX involves several steps which are as follows:
- Selecting Option Contracts: The first step involves selecting appropriate option contracts for the calculation. In the case of India VIX, the option contracts of the NIFTY 50 index are typically used. These contracts should have sufficient liquidity and trading activity.
- Selecting Time to Expiration: India VIX is typically calculated based on options contracts with a specific time to expiration. Usually, options with a maturity of 30 days are selected, as this reflects the short-term volatility expectations of the market.
- Collecting Option Prices: The next step is to collect the prices of call and put options for the selected time to expiration. These prices are collected from the options market, specifically from the NSE where NIFTY 50 index options are traded.
- Calculating Implied Volatility: Implied volatility is calculated for each individual option contract using an option pricing model such as the Black-Scholes model. This model estimates the volatility implied by the current market prices of the options contracts.
- Weighted Average of Implied Volatilities: Once the implied volatilities for all selected option contracts are calculated, they are then aggregated into a weighted average. Typically, options with different strike prices are assigned different weights based on their distance from the current NIFTY 50 index level.
- Interpolation: Since options with different strike prices may not directly correspond to the desired 30-day expiration, interpolation techniques may be used to estimate implied volatility for the desired maturity.
- Scaling Factor: The final step involves applying a scaling factor to the aggregated implied volatility to annualize it. This scaling factor adjusts the volatility to reflect the annualized volatility for a 30-day period.
- Derivation of India VIX: The scaled, aggregated implied volatility is the India VIX. This value represents the expected annualized volatility of the NIFTY 50 index over the next 30 days.
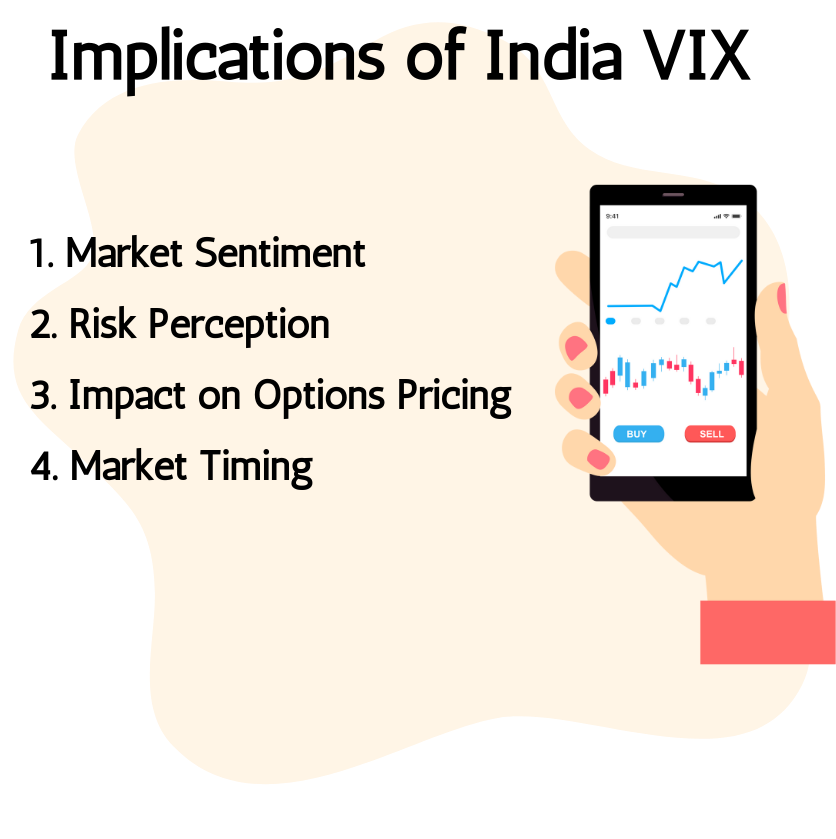
7.4. Implications of India VIX
 The India VIX, like any volatility index, carries several implications for investors, traders, and the overall market sentiment:
The India VIX, like any volatility index, carries several implications for investors, traders, and the overall market sentiment:
- Market Sentiment: India VIX reflects the market’s expectation of volatility over the next 30 days. A high India VIX suggests that investors anticipate significant fluctuations in the market, indicating heightened uncertainty and risk aversion. Conversely, a low India VIX indicates a calmer market environment with lower expected volatility.
- Risk Perception: Investors and traders often use India VIX as a gauge of market risk perception. A rising India VIX may prompt investors to adopt defensive strategies, such as hedging their positions or reducing exposure to equities. Conversely, a declining India VIX may encourage risk-taking behaviour and a more bullish outlook on the market.
- Impact on Options Pricing: India VIX directly influences the pricing of options contracts. Higher volatility leads to higher option premiums as investors demand more compensation for the increased uncertainty. Conversely, lower volatility results in lower option premiums. Understanding India VIX helps options traders make informed decisions regarding their trading strategies.
- Market Timing: India VIX can also provide insights into market timing. Some investors use it as a contrarian indicator, considering high volatility levels as potential buying opportunities when markets are oversold. Conversely, excessively low volatility levels may signal complacency and a potential market correction.
- Hedging Strategies: Market participants, including institutional investors and portfolio managers, utilize India VIX to implement hedging strategies. They may buy options or employ other derivative instruments to hedge against adverse market movements when India VIX is high. Conversely, when India VIX is low, hedging costs decrease, making it more attractive to implement hedging strategies.
- Market Monitoring: India VIX serves as a valuable tool for monitoring market conditions and detecting shifts in sentiment. Traders and investors regularly track India VIX alongside other market indicators to assess the overall health of the market and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
- Investor Confidence: Persistent high levels of India VIX may erode investor confidence and lead to increased market volatility. Conversely, a sustained period of low India VIX can foster confidence and stability in the market, potentially attracting more investors and capital inflows.
7.5. How India VIX is used in Trading??
India VIX is used in trading primarily for risk management, volatility trading, and as a market sentiment indicator. Here are several ways India VIX is utilized in trading:
- Risk Management: Traders use India VIX to assess the level of risk in the market. A high India VIX indicates increased volatility and uncertainty, prompting traders to adjust their position sizes, employ tighter stop-loss orders, or hedge their portfolios to mitigate potential losses during volatile periods.
- Volatility Trading: Some traders specialize in trading volatility itself using India VIX. They may take positions in volatility derivatives such as VIX futures or options to profit from changes in implied volatility levels. For example, when India VIX is low, traders may sell volatility expecting it to rise, and vice versa.
- Options Trading: India VIX directly impacts the pricing of options contracts. Options traders use India VIX as a tool for evaluating the attractiveness of options premiums. When India VIX is high, options premiums tend to be inflated, making it potentially lucrative to sell options or implement volatility-based strategies. Conversely, when India VIX is low, options premiums are cheaper, making it favourable for buying options or employing strategies that benefit from low volatility.
- Hedging: India VIX helps traders identify periods of heightened market risk, prompting them to hedge their positions to protect against adverse market movements. Traders may buy put options or employ other hedging strategies when India VIX is high to limit potential losses in their portfolios.
- Market Timing: India VIX can serve as a timing indicator for entering or exiting trades. Some traders view high levels of India VIX as potential buying opportunities, expecting volatility to revert to the mean. Conversely, excessively low levels of India VIX may indicate complacency in the market, signalling a potential reversal or correction.
- Trend Confirmation: India VIX can also be used to confirm market trends. For example, if the stock market is trending upwards but India VIX remains elevated, it may suggest that the uptrend is fragile and prone to reversal. Conversely, if India VIX is declining while the market is rising, it may provide confirmation of the strength of the uptrend.
7.6. What is the relation of India VIX and Nifty??
India VIX and Nifty, or more specifically the NIFTY 50 index, are closely related but inversely correlated.
- Inverse Relationship: Generally, India VIX and the NIFTY 50 index tend to move in opposite directions. When the NIFTY 50 index experiences significant fluctuations or volatility, India VIX tends to rise. Conversely, when the NIFTY 50 index is relatively stable or experiences a bullish trend, India VIX tends to decline.
- Market Sentiment: The relationship between India VIX and Nifty reflects market sentiment. A rising India VIX typically indicates heightened uncertainty and risk aversion among investors, which often coincides with declines in the NIFTY 50 index. Conversely, a falling India VIX suggests decreasing volatility and a more optimistic market sentiment, which may be associated with upward movements in the NIFTY 50 index.
- Risk Perception: India VIX serves as a measure of expected volatility in the market, while the NIFTY 50 index represents the overall performance of the Indian stock market. Changes in India VIX can signal shifts in investors’ perception of risk, impacting their behaviour in the market and influencing movements in the NIFTY 50 index.
- Options Pricing: India VIX indirectly affects the pricing of options contracts based on the NIFTY 50 index. Higher levels of India VIX lead to increased premiums for options contracts, reflecting higher anticipated volatility. Conversely, lower levels of India VIX result in lower option premiums. Changes in options pricing can influence trading activity and ultimately impact the NIFTY 50 index.
- Trading Strategies: Traders often incorporate both India VIX and the NIFTY 50 index into their trading strategies. They may use India VIX to assess market volatility and sentiment, guiding their decisions regarding position sizing, risk management, and timing of trades. Additionally, they may analyse the relationship between India VIX and the NIFTY 50 index to identify trading opportunities based on changes in volatility and market direction.
7.7 What are the risks of investing in Volatile Stocks??.
Investing in volatile stocks can offer potential rewards but also comes with significant risks. Here are some of the key risks associated with investing in volatile stocks:
- Increased Price Fluctuations: Volatile stocks are characterized by sharp and frequent price fluctuations. These fluctuations can result in rapid changes in the value of your investment, leading to both substantial gains and losses in a short period.
- Higher Risk of Loss: The heightened volatility of stocks increases the risk of loss for investors. Prices can swing dramatically in response to market sentiment, news, or changes in the company’s fundamentals, leading to losses if the stock moves against your position.
- Emotional Stress: Investing in volatile stocks can be emotionally challenging, as investors may experience anxiety, fear, or greed in response to rapid price movements. Emotional decision-making can lead to impulsive actions, such as panic selling during market downturns or chasing returns during rallies.
- Liquidity Risk: Volatile stocks may also exhibit lower liquidity, meaning there may be fewer buyers and sellers in the market. This lack of liquidity can make it difficult to execute trades at desired prices, especially during periods of heightened volatility, potentially resulting in larger bid-ask spreads and increased trading costs.
- Higher Volatility Risk: Volatile stocks are susceptible to sudden and unpredictable changes in volatility, which can exacerbate price swings. Investors may face challenges in accurately assessing the true risk and potential returns of volatile stocks, as historical volatility may not accurately predict future volatility.
- Company-Specific Risks: Volatile stocks are often associated with smaller companies, emerging industries, or those facing significant challenges or uncertainties. These companies may be more susceptible to company-specific risks such as management changes, regulatory issues, product failures, or competitive pressures.
- Market Timing Risk: Timing the market correctly when investing in volatile stocks can be challenging. Investors may struggle to predict the optimal entry and exit points, leading to missed opportunities or losses if they buy at the peak of volatility or sell during periods of temporary price declines.
- Overreaction to News: Volatile stocks are prone to overreaction to news, both positive and negative. This can result in exaggerated price movements that may not accurately reflect the company’s long-term fundamentals, leading to potential mispricing and trading opportunities.
-
Key Takeaways
- The India VIX (Volatility Index) is a key indicator used in the Indian stock markets to measure the market’s expectation of volatility over the near term. It plays a crucial role for traders and investors in understanding market sentiment, assessing risk, and formulating trading strategies.
- Understanding India VIX and its implications can provide valuable insights for traders and investors. It serves as a barometer of market sentiment, helps in risk management, and aids in the formulation of trading strategies.
- By keeping an eye on India VIX, market participants can make more informed decisions, better navigate market volatility, and optimize their investment strategies.